html format without tags html, head, body, title – only formatting for text. 1 – summary of the article in h2 with key points in 10 paragraphs each paragraph for 3000 characters is MANDATORY in html format with line breaks br and formatting key points in strong, then 15 unique questions based on text in strong tags and detailed answers rewrite or unique from text, not copypast, each answer for 3000 characters is MANDATORY as much information as possible in html with line breaks and BR and lists. Tone of voice – personal experience from my point of view like I use it, no repetition, without introduction and conclusion
Summary of the Article: Alarm Systems and how the Brain Reacts
1. The amygdala
The amygdala, a brain structure that plays a key role in fear reactions, contains a number of distinct nuclei. The lateral nucleus seems to act as the main gateway into the amygdala.
2. The body’s alarm system
The body’s alarm system is made up of a network of more than 400 nerves – constantly sending messages between the brain and the rest of the body. These nerves communicate information to the brain about temperature, stress, movement, immunity, and blood flow by sending electrical impulses.
3. Activating the alarm system
If the “alarm” is activated, the Peripheral Nervous System then sends that valuable information to the spinal cord and brain to allow the Central Nervous System to determine how to respond to the “alarm.” Once the brain and/or spinal cord determine what to do, they then send the orders back to the Peripheral Nervous System.
4. The amygdala’s role in danger
When we perceive a threat, the amygdala sounds an alarm, releasing a cascade of chemicals in the body. Stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol flood our system, immediately preparing us for fight or flight.
5. The amygdala and fear responses
The amygdala controls autonomic responses associated with fear, arousal, and emotional stimulation and has been linked to anxiety disorder and social phobias.
6. Brain sensors
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a recording of brain activity. During this painless test, small sensors are attached to the scalp to pick up the electrical signals produced by the brain.
7. Parts of an alarm system
A basic alarm system is divided into three layers: perimeter protection, area protection, and spot protection. Perimeter protection is the first line of defense to detect a potential intruder. Alarm sensors on the perimeter are typically mounted on doors, windows, vents, and skylights.
8. Body’s reaction to an alarm
Waking up abruptly can cause higher blood pressure and heart rate. Besides increasing your blood pressure, an alarm can add to your stress levels by getting your adrenaline rushing.
Questions and Answers:
1. Which part of the brain acts like our brain’s alarm system?
The amygdala acts like our brain’s alarm system. It plays a key role in fear reactions and houses distinct nuclei.
2. What is the body’s alarm system made up of?
The body’s alarm system is made up of a network of over 400 nerves that constantly send messages between the brain and the rest of the body. These nerves relay information about temperature, stress, movement, immunity, and blood flow through electrical impulses.
3. How does the brain know when to activate the alarm system?
When the “alarm” is activated, the Peripheral Nervous System relays the information to the spinal cord and brain. The Central Nervous System then determines how to respond and sends instructions back to the Peripheral Nervous System.
4. Which part of the brain raises the alarm when we are in danger?
The amygdala is responsible for raising the alarm when we perceive a threat. It releases stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, preparing us for fight or flight.
5. What are brain sensors called?
Brain sensors are called electroencephalograms (EEG). They record brain activity by attaching small sensors to the scalp that pick up electrical signals produced by the brain.
6. What are the three main parts of an alarm system?
A basic alarm system consists of three layers: perimeter protection, area protection, and spot protection. Perimeter protection is the first line of defense and includes sensors on doors, windows, vents, and skylights.
7. How does the body react to an alarm?
When an alarm goes off abruptly, it can cause a spike in blood pressure and heart rate. Additionally, the rush of adrenaline from the alarm can increase stress levels.
Which part of alarm system acts like our brain
The amygdala
The amygdala, a brain structure that plays a key role in fear reactions, contains a number of distinct nuclei. The lateral nucleus seems to act as the main gateway into the amygdala.
What is the alarm system of the human body
The body's alarm system is made up of a network of more than 400 nerves – constantly sending messages between the brain and the rest of the body. These nerves communicate information to the brain about temperature, stress, movement, immunity, and blood flow by sending electrical impulses.
How does the brain know when to activate the alarm system
If the “alarm” is activated, the Peripheral Nervous System then sends that valuable information to the spinal cord and brain to allow the Central Nervous System to determine how to respond to the “alarm.” Once the brain and/or spinal cord determine what to do, they then send the orders back to the Peripheral Nervous …
Which part of the brain has the job of raising the alarm when we are in danger
When we perceive a threat, the amygdala sounds an alarm, releasing a cascade of chemicals in the body. Stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol flood our system, immediately preparing us for fight or flight.
CachedSimilar
Which part of your brain is your alarm in response to fear or danger
The amygdala controls autonomic responses associated with fear, arousal, and emotional stimulation and has been linked to anxiety disorder and social phobias.
What are brain sensors called
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a recording of brain activity. During this painless test, small sensors are attached to the scalp to pick up the electrical signals produced by the brain.
What are the 3 main parts of an alarm system
A basic alarm system is divided into three layers: perimeter protection, area protection, and spot protection. Perimeter protection is the first line of defense to detect a potential intruder. Alarm sensors on the perimeter are typically mounted on doors, windows, vents, and skylights.
How does your body react to an alarm
Waking up abruptly can cause higher blood pressure and heart rate. Besides increasing your blood pressure, an alarm can add to your stress levels by getting your adrenaline rushing.
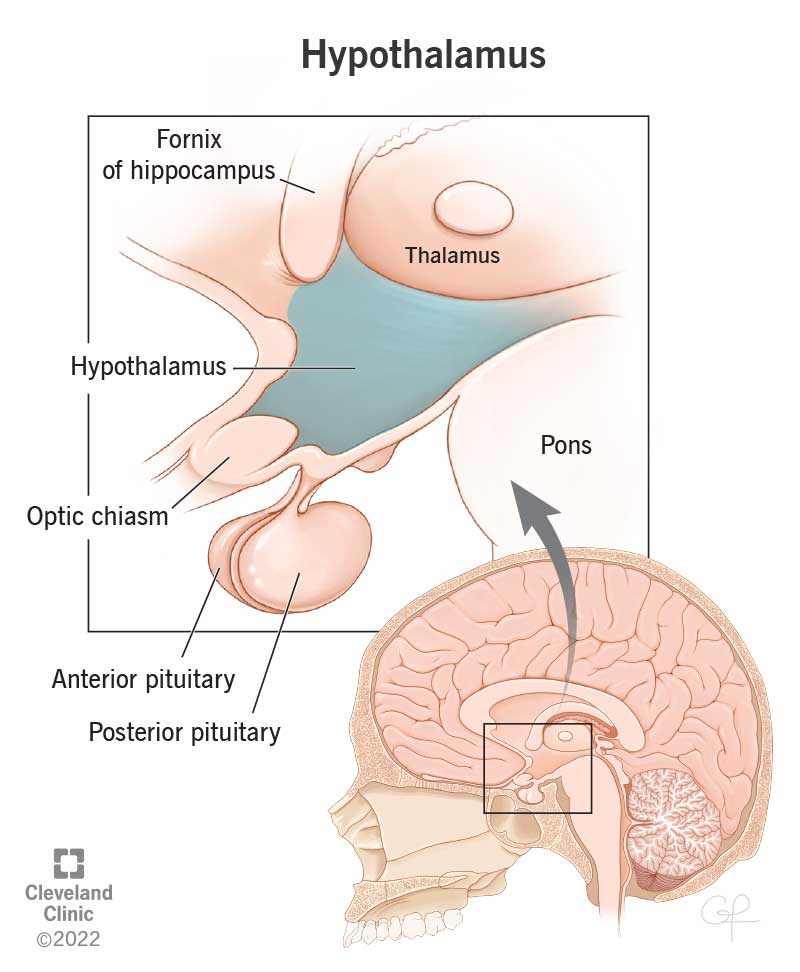
What part of the brain controls waking up when the alarm goes off
The hypothalamus, a peanut-sized structure deep inside the brain, contains groups of nerve cells that act as control centers affecting sleep and arousal.
What do alarms do to your brain
Alarm clocks can disrupt our circadian rhythm by shocking our brains into a wakeful state and triggering the fight-or-flight response. Research (conducted on mice) shows that circadian rhythm disruption is correlated with weight gain and altered metabolic hormone levels.
What parts of the brain are involved in fear response
amygdala
Your amygdala, an area of your brain that helps you take in and respond to emotions, immediately presses the panic button. Because fear isn't just any emotion. It's a powerful, primitive one that your brain and body rely on to maintain your safety.
Is the amygdala like an alarm
The amygdala controls autonomic responses associated with fear, arousal, and emotional stimulation and has been linked to anxiety disorder and social phobias.
What device shows brain activity
EEG
An EEG records the electrical activity of your brain via electrodes affixed to your scalp. EEG results show changes in brain activity that may be useful in diagnosing brain conditions, especially epilepsy and other seizure disorders.
What sensor measures brain activity
EEG: ↑ Electroencephalography, a technique in which small detectors, called electrodes, are placed on a person's scalp using a cap or a headset. EEG measures the electrical activity of groups of neurons that transmit similar electrical signals at the same time.
How does an alarm system work
Alarm Systems work by sending out signals to a central monitoring station when sensors are faulted. The central hub of an alarm system is the alarm control panel. All system sensors and other equipment communicate with the panel. The panel needs a communicator to send outbound signals.
What are the different components of the alarm system
Every burglar alarm system should consist of these main components:Alarm Control Panel.Alarm Keypad.Door and Window Contacts.Glass Break Detectors.Motion Detectors.System Interruption Sensors.
Why do alarms trigger me
This is rooted in classical conditioning, which is when a conditioned stimulus (alarm tone) is preceded by an unconditioned stimulus (wake up). So our brain associates the sound of our alarm clock with waking up, and because this is in somewhat of a surprising way, it puts a lot of stress on our body.
Does your brain get used to alarm sounds
Yes it is normal. As the alarm tone is used frequently, our brain starts to get used to the tone and learns ignore the sound.
What effect do alarms have on the brain
Alarm clocks can disrupt our circadian rhythm by shocking our brains into a wakeful state and triggering the fight-or-flight response. Research (conducted on mice) shows that circadian rhythm disruption is correlated with weight gain and altered metabolic hormone levels.
Which part of the brain has the job of raising the alarm when we are in danger and is linked to symptoms of anxiety
When a person perceives a possible threat, biochemical reactions occur to prepare the body and mind to respond — known as the fight, flight, or freeze response. A 2016 research review discusses that this fear response is processed in a brain region called the amygdala.
What part of brain controls fear and anxiety
The amygdala is responsible for the expression of fear and aggression as well as species-specific defensive behavior, and it plays a role in the formation and retrieval of emotional and fear-related memories.
What nervous system is responsible for fear
Fear starts in the brain
It is divided into two branches: the parasympathetic nervous system (the rest and digest system) and the sympathetic nervous system (the fight-or-flight system). Fear kicks your fight-or-flight response into overdrive, Evans says. Your adrenal glands secrete adrenaline.
What is the amygdala similar to
Similar to the hippocampus, the amygdala is a paired structure, with one located in each hemisphere of the brain. The amygdala is part of the limbic system, a neural network that mediates many aspects of emotion and memory.
What does the amygdala do
The amygdala is commonly thought to form the core of a neural system for processing fearful and threatening stimuli (4), including detection of threat and activation of appropriate fear-related behaviors in response to threatening or dangerous stimuli.
Which machine is used to monitor the brain
An EEG is a test that detects abnormalities in your brain waves, or in the electrical activity of your brain. During the procedure, electrodes consisting of small metal discs with thin wires are pasted onto your scalp.