Summary of Article: Laws Protecting Personal Privacy
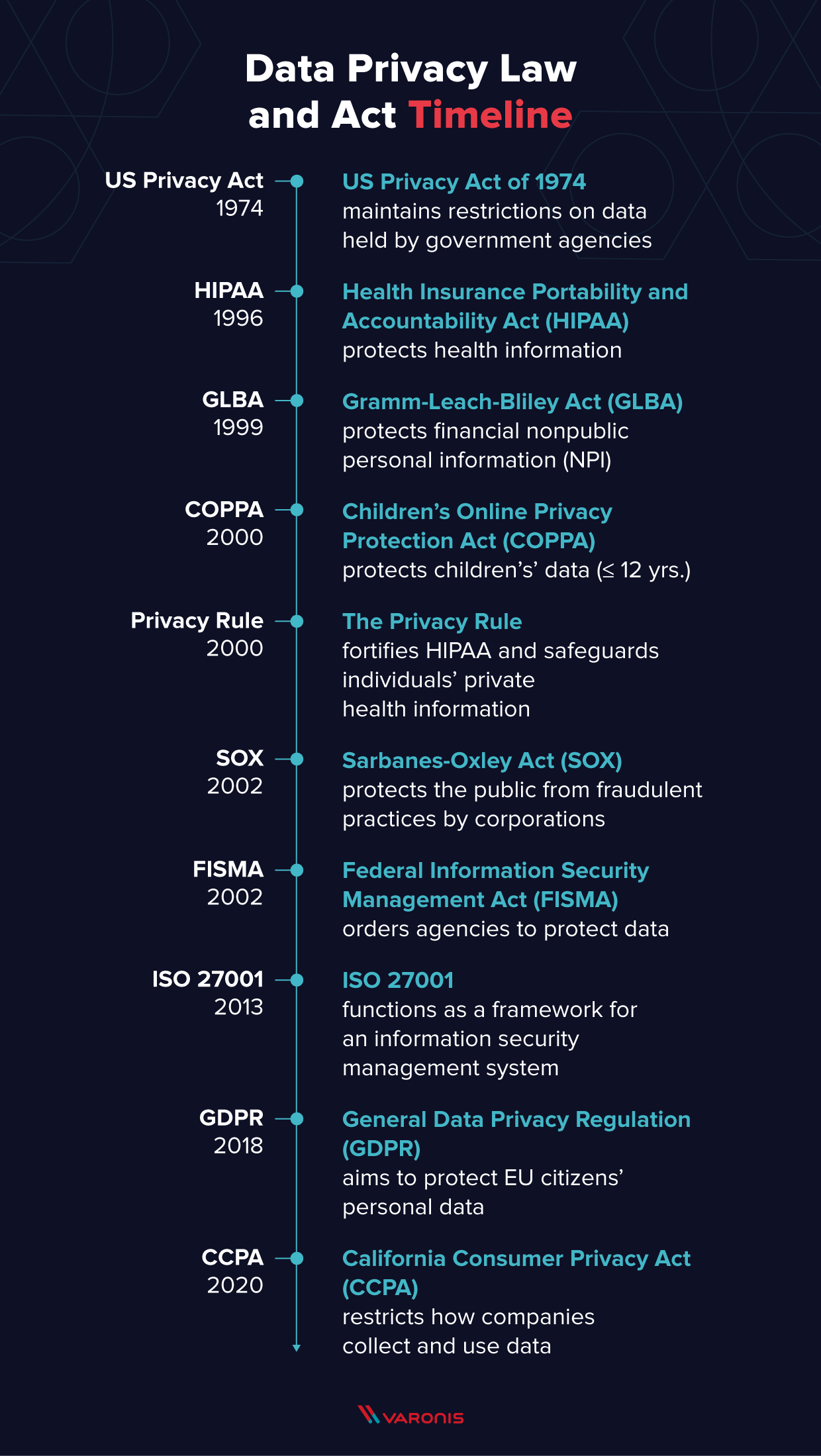
1. The Privacy Act of 1974: This law establishes fair information practices for the collection, use, and dissemination of information about individuals by federal agencies.
2. Privacy Laws in California: The California Constitution recognizes privacy as an inalienable right. CA SB 1386 requires companies to report any exposure of sensitive information of California citizens.
3. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): This law grants consumers rights over their personal data, including the right to correct inaccurate data and the right to limit the use and disclosure of sensitive information.
4. Privacy Law and Personally Identifiable Information: Privacy law regulates the storage, use, and sharing of personally identifiable information, healthcare information, and financial information held by governments, organizations, or individuals.
5. The 14th Amendment and Privacy: The right to privacy is implied by the guarantee of due process in the Fourteenth Amendment, protecting individuals from undue control over their private lives.
6. Privacy and the US Constitution: Although not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution, the Supreme Court has recognized the right to privacy through several amendments.
7. Privacy Acts in the US: The Privacy Act of 1974 protects records containing personal identifiers such as names or social security numbers.
15 Questions Based on the Text:
1. What laws protect personal privacy? The Privacy Act of 1974 and various state privacy laws.
2. Are there privacy laws in the US? California has strict privacy laws, and other states have adopted similar measures.
3. What is the basic privacy law? The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) provide fundamental privacy rights.
4. What type of law is privacy? Privacy law encompasses regulations related to the collection and use of personal information.
5. How does the 14th Amendment protect privacy? The 14th Amendment implies the right to privacy through the guarantee of due process.
6. What is the 14th Amendment right to privacy? The 14th Amendment protects individuals from the state’s undue control over their private lives.
7. Is privacy protected in the US Constitution? Although not explicitly stated, the Supreme Court recognizes the right to privacy through certain amendments.
8. What are the privacy acts in the US? One of the key privacy acts is the Privacy Act of 1974, which safeguards personal records.
What laws protect personal privacy
The Privacy Act of 1974, as amended, 5 U.S.C. § 552a , establishes a code of fair information practices that governs the collection, maintenance, use, and dissemination of information about individuals that is maintained in systems of records by federal agencies.
CachedSimilar
Are there privacy laws in the US
California. The California Constitution articulates privacy as an inalienable right. CA SB 1386 expands on privacy law and guarantees that if a company exposes a Californian's sensitive information this exposure must be reported to the citizen. This law has inspired many states to come up with similar measures.
CachedSimilar
What is the basic privacy law
The CCPA was updated with a second act—the California Privacy Rights Act—which was passed in 2020 and took effect in 2023. This extended the rights of consumers to include the right to correct inaccurate data a business collected about them and the right to limit the use and disclosure of sensitive data.
What type of law is privacy
Privacy law is the body of law that deals with the regulating, storing, and using of personally identifiable information, personal healthcare information, and financial information of individuals, which can be collected by governments, public or private organisations, or other individuals.
How does the 14th Amendment protect privacy
In the Fourteenth Amendment, the right to privacy is implied by the guarantee of due process for all individuals, meaning that the state cannot exert undue control over citizens' private lives.
What is the 14th Amendment right to privacy
In the Fourteenth Amendment, the right to privacy is implied by the guarantee of due process for all individuals, meaning that the state cannot exert undue control over citizens' private lives.
Is privacy protected in the US Constitution
The right to privacy is not mentioned in the Constitution, but the Supreme Court has said that several of the amendments create this right.
What are the privacy acts in the US
The Privacy Act of 1974, as amended to present, including Statutory Notes (5 U.S.C. 552a), Protects records about individuals retrieved by personal identifiers such as a name, social security number, or other identifying number or symbol.
What are the four categories of privacy law
The four Ps of privacy are people, places, platforms, and purposes.
Do we have a constitutional right to privacy
The right to privacy is not mentioned in the Constitution, but the Supreme Court has said that several of the amendments create this right.
What are the four types of privacy rights
The four Ps of privacy are people, places, platforms, and purposes.
What does the 4th Amendment say about privacy
The Constitution, through the Fourth Amendment, protects people from unreasonable searches and seizures by the government. The Fourth Amendment, however, is not a guarantee against all searches and seizures, but only those that are deemed unreasonable under the law.
Is the right to privacy in the 10th Amendment
The authors of the Bill of Rights could not list every individual right. So, they added the Ninth and Tenth Amendments to cover all those not listed. For example, one right not specifically listed is "privacy." Many people consider privacy to be covered under the Ninth and Tenth Amendments.
What does the 9th Amendment say about the right to privacy
The Ninth Amendment provides: 'The enumeration in the Constitution, of certain rights, shall not be construed to deny or disparage others retained by the people. '” Finally, the Court concluded that privacy within marriage was a personal zone off limits to the government.
What does the 14th Amendment say
No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.
What are the four states of privacy
While examples of all of the privacy states developed by Westin (reserve, solitude, intimacy, and anonymity) were mentioned, younger adults tended to define privacy in terms of what Westin calls reserve, or the desire to limit disclosures to others [12].
What are the 7 principles of privacy policy
The principles are: Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency; Purpose Limitation; Data Minimisation; Accuracy; Storage Limitations; Integrity and Confidentiality; and Accountability.
What are the three types of privacy rights
Digital privacy can be defined under three sub-related categories: information privacy, communication privacy, and individual privacy.
Does the Constitution protect privacy
The right to privacy is not mentioned in the Constitution, but the Supreme Court has said that several of the amendments create this right.
Is privacy in the 5th amendment
The Fourth Amendment protects the right of privacy against unreasonable searches and seizures by the government. The Fifth Amendment provides for the right against self-incrimination, which justifies protection of private information.
How does the 14th amendment protect privacy
In the Fourteenth Amendment, the right to privacy is implied by the guarantee of due process for all individuals, meaning that the state cannot exert undue control over citizens' private lives.
Does the 4th amendment protect the right to privacy
The Constitution, through the Fourth Amendment, protects people from unreasonable searches and seizures by the government. The Fourth Amendment, however, is not a guarantee against all searches and seizures, but only those that are deemed unreasonable under the law.
Does the 4th Amendment protect the right to privacy
The Constitution, through the Fourth Amendment, protects people from unreasonable searches and seizures by the government. The Fourth Amendment, however, is not a guarantee against all searches and seizures, but only those that are deemed unreasonable under the law.
What does the 15th Amendment protect
Passed by Congress February 26, 1869, and ratified February 3, 1870, the 15th Amendment granted African American men the right to vote.
What Amendment is 16
Passed by Congress on July 2, 1909, and ratified February 3, 1913, the 16th amendment established Congress's right to impose a Federal income tax.