Internal controls are essential for safeguarding customer information and maintaining data security within an organization. The three most common internal controls are:
- Access controls: These controls ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive customer information. This can include implementing password protection, user authentication processes, and limiting access to certain data based on job roles and responsibilities.
- Segregation of duties: This control involves separating certain tasks and responsibilities within the organization to prevent any single individual from having complete control over customer information. By dividing responsibilities, it reduces the risk of unauthorized access or misuse of data.
- Regular monitoring and auditing: This control involves regularly reviewing and auditing systems, processes, and employee activities to ensure compliance with data security policies and identify any potential vulnerabilities or breaches. Monitoring can include reviewing access logs, conducting periodic assessments, and performing internal security audits.
By implementing these internal controls, organizations can significantly enhance the security of customer information and mitigate the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
Customer information is a valuable asset that needs to be protected due to several reasons:
- Privacy concerns: Customers trust businesses with their personal information, and it is the responsibility of the organization to safeguard this sensitive data. Failure to protect customer information can lead to a breach of privacy, which can erode trust and damage the reputation of the company.
- Legal and regulatory requirements: Many industries have specific laws and regulations that mandate the protection of customer information. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in significant fines, legal actions, and reputational damage.
- Financial implications: Data breaches can be costly for businesses. The cost of investigating and remediating a breach, potential lawsuits, lost revenue, and damage to the brand can have long-lasting financial implications. Protecting customer information helps mitigate these risks.
- Competitive advantage: In the digital age, customer trust and data security are becoming crucial competitive differentiators. Companies that prioritize customer information protection can attract and retain customers who value their privacy and security.
When it comes to securing customer information, one of the most critical aspects is identifying the types of information that need to be protected. Here are some common types of customer data that require secure handling:
- Personal information: This includes data such as names, addresses, phone numbers, social security numbers, and birthdates. Protecting personal information is crucial to prevent identity theft and fraud.
- Financial information: Credit card numbers, bank account details, and financial transaction records should be secured to prevent unauthorized access and fraudulent activities.
- Health records: In industries like healthcare, protecting patient health records is vital to ensure compliance with privacy regulations and maintain patient confidentiality.
- Account passwords: Encrypted storage and secure password management practices are necessary to protect user accounts from unauthorized access.
- Website databases: Any databases containing customer information should be secured to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Intellectual property: For businesses dealing with proprietary information or trade secrets, protecting intellectual property is essential to maintain a competitive advantage.
- Employee information: Employee records, including personal and financial information, should be secured to prevent identity theft and protect employee privacy.
- Business plans: Confidential business information, such as future strategies, financial projections, and market research, should be kept secure to prevent competitive disadvantage.
What are the types of information that need to be secured
The most sensitive information to protect includes your bank account numbers, social security number, pin numbers, credit card numbers, and passwords.
How do you keep customer information secure
10 best practices to protect customer data privacyKnow what data you are collecting.Only collect essential information.Create and publish a transparent data usage and privacy policy.Encrypt all sensitive user data.Protect against phishing scams.Update all software.Implement multi-factor authentication.
Cached
Why should customer information be protected
Protecting your customer's data is important for one huge reason: your business depends on it. If your company doesn't take steps to protect customer data, you'll be vulnerable to hacks, which could lead to loss of consumer confidence, customers leaving, fines, lawsuits, and more.
Cached
What are 4 types of information security
There are four types of information technology security you should consider or improve upon:Network Security.Cloud Security.Application Security.Internet of Things Security.
What are the 5 elements of information security
5 Key Elements of a Modern Cybersecurity FrameworkIdentify.Protect.Detect.Respond.Recover.
What 3 types of controls are required to safeguard customer information
The Safeguards Rule requires covered financial institutions to develop, implement, and maintain an information security program with administrative, technical, and physical safeguards designed to protect customer information.
What data needs to be protected
Personal Information. Personal information is any data related to an individual, such as name, address, phone number, Social Security Number, birth date, and more.Financial Information.Account Passwords.Health Records.Website Databases.Intellectual Property.Employee Information.Business Plans.
What is customer information protection
Consumer privacy, also known as customer privacy, involves the handling and protection of the sensitive personal information provided by customers in the course of everyday transactions.
What are the five 5 components of information security
The U.S. Department of Defense has promulgated the Five Pillars of Information Assurance model that includes the protection of confidentiality, integrity, availability, authenticity, and non-repudiation of user data.
What are the 3 categories to information security
When we discuss data and information, we must consider the CIA triad. The CIA triad refers to an information security model made up of the three main components: confidentiality, integrity and availability.
What are the 7 P’s of information security
We outline the anatomy of the AMBI-CYBER architecture adopting a balanced scorecard, multistage approach under a 7Ps stage gate model (Patient, Persistent, Persevering, Proactive, Predictive, Preventive, and Preemptive).
What are the 3 most common internal controls
Internal controls fall into three broad categories: detective, preventative, and corrective.
What are the three 3 types of access control
Types of access control systemsDiscretionary access control (DAC) A discretionary access control system, on the other hand, puts a little more control back into leadership's hands.Rule-based access control.Identity-based access control.
What are the 7 golden rules of data protection
Necessary, proportionate, relevant, adequate, accurate, timely and secure: Ensure that information you share is necessary for the purpose for which you Page 2 are sharing it, is shared only with those individuals who need to have it, is accurate and up-to-date, is shared in a timely fashion, and is shared securely (see …
What are the 4 data protection principles
Accuracy. Storage limitation. Integrity and confidentiality (security) Accountability.
What are the three types of information to protect
When we discuss data and information, we must consider the CIA triad. The CIA triad refers to an information security model made up of the three main components: confidentiality, integrity and availability. Each component represents a fundamental objective of information security.
What are the 4 types of information security
There are four types of information technology security you should consider or improve upon:Network Security.Cloud Security.Application Security.Internet of Things Security.
What are the 4 levels of information classification
Data Classification Levels
These can be adopted by commercial organizations, but, most often, we find four levels, Restricted, Confidential, Internal, Public.
What are the 3 A’s of information security
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) is a three-process framework used to manage user access, enforce user policies and privileges, and measure the consumption of network resources.
What are the 5 main internal controls
There are five interrelated components of an internal control framework: control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring.
What are the 4 types of internal controls
Preventive ControlsSeparation of duties.Pre-approval of actions and transactions (such as a Travel Authorization)Access controls (such as passwords and Gatorlink authentication)Physical control over assets (i.e. locks on doors or a safe for cash/checks)
What are the three types of sensitive information
There are three main types of sensitive information:Personal Information. Also called PII (personally identifiable information), personal information is any data that can be linked to a specific individual and used to facilitate identity theft.Business Information.Classified Information.
What are the four 4 main access control model
The 4 main access control models are:
Discretionary access control (DAC) Mandatory access control (MAC) Role-based access control (RBAC) Rule-based access control (RuBAC)
Which are the 4 basic principles of data privacy
Accuracy. Storage limitation. Integrity and confidentiality (security) Accountability.
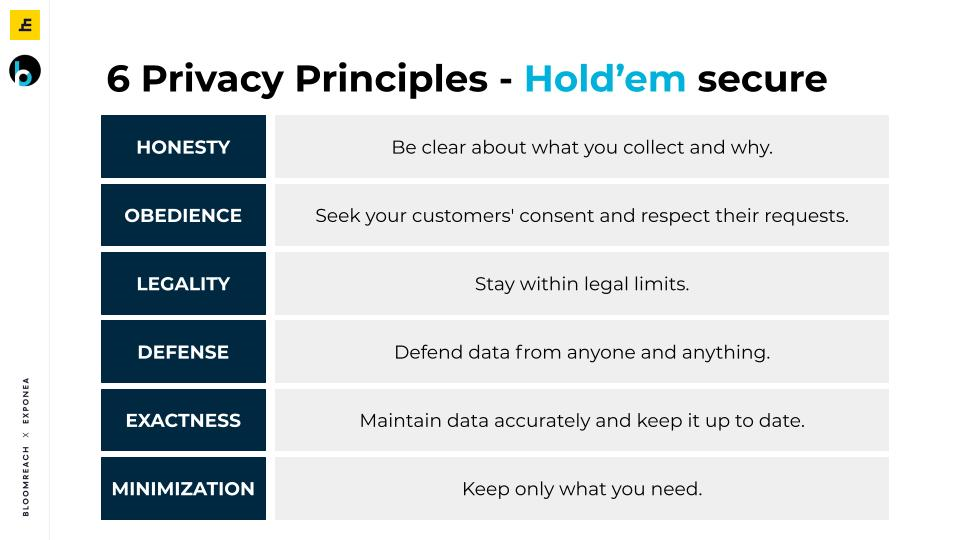
What are the six 6 essential data protection methods
We take a look at each principle in this blog, and provide advice on how they should fit within your GDPR compliance practices.Lawfulness, fairness and transparency.Purpose limitation.Data minimisation.Accuracy.Storage limitation.Integrity and confidentiality.