Summary of Article: TT and TN Earthing Systems
TT System: In a TT earthing system, the transformer neutral is earthed and the frame is also earthed.
TN System: In a TN earthing system, the transformer neutral is earthed and the frame is connected to the neutral.
IT System: In an IT earthing system, the transformer neutral is unearthed and the frame is earthed.
TT vs TN System: The main difference between a TT system and a TN system is that in a TT system, the source and the load are separately connected to earth, with no connection between earth and neutral. In a TN system, there are different variations such as TN-C, TN-S, and TN-C-S, which have different connections for earth and neutral.
Three Types of Earthing Systems: The IEC 60364 standard defines three types of earthing systems – TT, IT, and TN.
Earth Rod in TT System: In a TT system, all exposed-conductive-parts and extraneous-conductive-parts of the installation must be connected to a common earth electrode.
Usage of TN Earthing: TN-C-S systems, where the earth conductor is used as the neutral conductor and a separate earth conductor is connected to a metallic structure buried in the ground, are often used in larger installations like multi-phase commercial or industrial buildings.
Major Types of Earthing: The major types of earthing are pipe earthing, plate earthing, and strip earthing.
Disadvantages of TT Earthing: The main disadvantage of the TT earthing system is the simultaneous failure of a residual current device (RCD) and a breakdown of a phase conductor to the earthed enclosure of an electrical appliance.
Disadvantages of TN Earthing: One of the disadvantages of the TN-S earthing system is its low power factor.
Questions and Answers:
1) What is TT and TN earthing?
TT earthing refers to a system where the transformer neutral and frame are earthed, while TN earthing refers to a system where the transformer neutral is earthed and the frame is connected to the neutral.
2) What does TT stand for in earthing systems?
‘TT’ stands for Terra, which translates to earth in French. The first ‘T’ in a TT earthing system refers to the earthing of the distribution transformer, and the second ‘T’ refers to the earth electrode installed at the consumer’s installation.
3) What is the difference between a TT system and a TNS system?
In a TT system, the source and the load are separately connected to earth, with no connection between earth and neutral. In a TNS system, there are different variations such as TN-C, TN-S, and TN-C-S, which have different connections for earth and neutral.
4) What are the three types of earthing systems?
The three types of earthing systems defined by the IEC 60364 standard are TT, IT, and TN systems.
5) Does a TT system need an earth rod?
Yes, in a TT system, all exposed-conductive-parts and extraneous-conductive-parts of the installation must be connected to a common earth electrode.
6) Where is TN earthing used?
TN earthing, specifically TN-C-S systems, are often used in larger installations like multi-phase commercial or industrial buildings.
7) What are the two major types of earthing?
The two major types of earthing are pipe earthing, plate earthing, and strip earthing.
8) What are the disadvantages of TT earthing system?
The main disadvantage of the TT earthing system is the simultaneous failure of a residual current device (RCD) and a breakdown of a phase conductor to the earthed enclosure of an electrical appliance.
9) What are the disadvantages of TN earthing system?
One of the disadvantages of the TN-S earthing system is its low power factor.
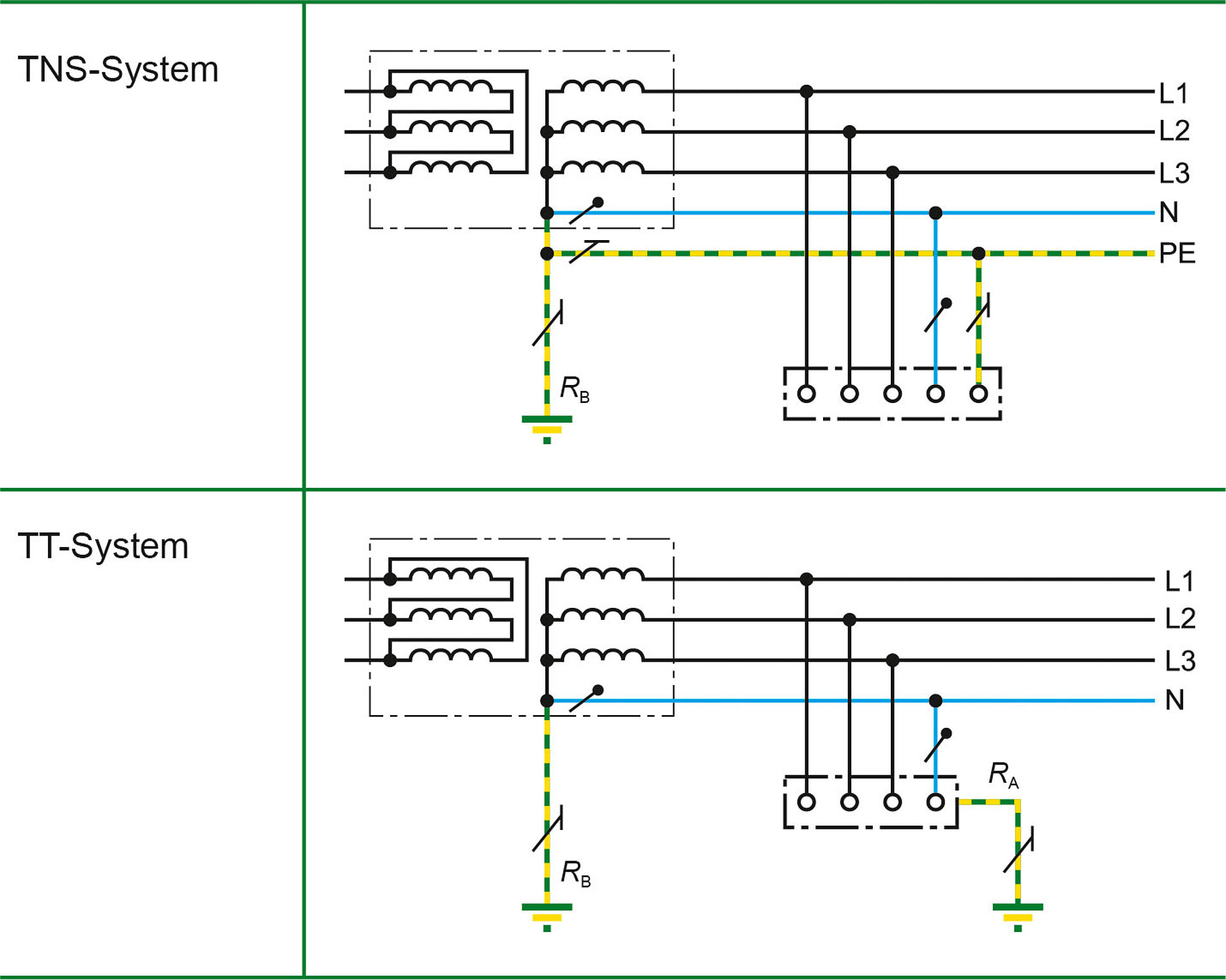
What is TT and TN earthing
1) TT: transformer neutral earthed and frame earthed. 2) TN: transformer neutral earthed, frame connected to neutral. 3) IT: unearthed transformer neutral, earthed frame.
Cached
What does TT stand for in earthing systems
'T' is French for Terra, which translates to earth. The first 'T' of a TT earthing system relates to the earthing of the distributors transformer, the second 'T' is the earth electrode installed at the consumers installation as shown in Figure 1.
Cached
What is the difference between a TT system and a TNS system
TT : the source and the load separately connected to earth, there is no connection between earth and neutral too. there is TN-C where common cable is used for earth and neutral, TN-S separate neutral and earth but same as source's earth, TN-C-S there is common point for earth and neutral but they both have cables.
What are the three types of earthing systems
The IEC 60364 standard has defined three types of Earthing Systems, namely TT, IT, and TN systems.
Does a TT system need an earth rod
In this system, all exposed-conductive-parts and extraneous-conductive-parts of the installation must be connected to a common earth electrode.
Where is TN earthing used
In this case, the earth conductor (C) is used as the neutral conductor, and there is also a separate earth conductor (S) that is connected to a metallic structure buried in the ground. TN-C-S systems are often used in larger installations, such as in multi-phase commercial or industrial buildings.
What are the 2 major types of earthing
There are three types of earthing, they are:Pipe earthing.Plate earthing.Strip earthing.
What are the disadvantages of TT earthing system
The only disadvantage of the TT earthing system is the simultaneous failure of a residual current device (RCD) and a breakdown of a phase conductor to the earthed enclosure of an electrical appliance.
What are the disadvantages of TN earthing system
Disadvantages of the TN-S Earthing SystemLow power factor (high inductance of long cable).Requires extra equal potential bonding.On occurrence of an insulation fault, the short-circuit current is high and may cause damage to equipment or electromagnetic disturbance.
What are the advantages of TNS earthing system
Advantages of TN-S Earthing System
TN-S is the safest system. Electromagnetic interference is low. It does not require earth electrode at site. TN-S earthing system could work with simple over current protection.
What size earth do you need for a TT system
Note: when, in a TT scheme, the installation earth electrode is beyond the zone of influence of the source earthing electrode, the c.s.a. of the PE conductor can be limited to 25 mm2 (for copper) or 35 mm2 (for aluminium).
What is the safest earthing system
TN-S
TN-S is the safest system. Electromagnetic interference is low. It does not require earth electrode at site. TN-S earthing system could work with simple over current protection.
What is the best earthing method
The pipe earthing is better than another type of earthing, because it can earth more leakage current, and the possibility of braking in the earth wire is minimum. Pipe Earthing: In this method the galvanized steel and perforated pipe of approved length and diameter in place upright in a permanently wet soil.
What are the 4 types of earthing systems
Types of EarthingPipe earthing.Plate earthing.Strip earthing.
Which type of earthing system is the best
Pipe earthing is the most common and best system of earthing as compared to other systems suitable for the same earth and moisture conditions. Pipe earthing is the best form of earthing and is very cheap in cost.
How deep should an earth rod be
8 feet
The ground rod must be driven into the soil to a depth that is sufficient to reach lower-resistance soil, typically 8 feet or more. The ground rod must also be spaced a sufficient distance from the structure to avoid interference with the lightning protection system.
Which type of earthing is most common and best type of earthing
Pipe earthing
Pipe earthing is the most common and best system of earthing as compared to other systems suitable for the same earth and moisture conditions. Pipe earthing is the best form of earthing and is very cheap in cost.
What are the 4 types of earthing
The four types of electric earthing systems are:Pipe earthing.Plate earthing.Strip or Wire earthing.Rod earthing.
What is the minimum earth size for TT system
Note: when, in a TT scheme, the installation earth electrode is beyond the zone of influence of the source earthing electrode, the c.s.a. of the PE conductor can be limited to 25 mm2 (for copper) or 35 mm2 (for aluminium).
Where is the best place to put an earth rod
Find a place for your ground rod outside that's near your home's electrical panel and at least 2 feet (0.61 m) away from the side of your house. Dig a 2–4 feet (0.61–1.22 m) deep hole and insert the rod inside.
What is the best earthing system
Marconite Earthing:
It is considered the world's best earthing system. Marconite is a conductive material that provides low resistance, stable and permanent solutions to engineers in a variety of difficult ground conditions.
How far does an earth rod need to go in the ground
8 feet
The ground rod must be driven into the soil to a depth that is sufficient to reach lower-resistance soil, typically 8 feet or more. The ground rod must also be spaced a sufficient distance from the structure to avoid interference with the lightning protection system.
How deep should an earth rod be buried
In the event that a rod must be laid flat, it must be buried at a depth of 30 inches. This is a common burial depth for most “made” electrodes. Plate and ground ring electrodes must also be installed at a minimum depth of 30 inches.
Why does a grounding rod have to be 8 feet
The NEC and UL require a ground rod to be at least 8 feet in length. This specification was obviously created by engineers that had never driven a ground rod or noticed that most people are not 8' tall. Longer rods are more dangerous to install and bow more when being driven.
How long does a ground rod need to be in the ground
8-foot
The only legal ground rod must be installed a minimum of 8-foot in the ground.