Summary of the Article
1. The alarm system in the brain is controlled by the amygdala. The amygdala triggers the natural alarm system when we experience a disturbing event, causing a fear response.
2. The security alarm system consists of three main parts. These are detectors, alarm control panel, and CMS. Different types of fire alarm monitoring systems include ionization, photoelectric, and combination alarms.
3. A basic alarm system has three layers of protection. These layers are perimeter protection, area protection, and spot protection. Perimeter protection is the first line of defense, with sensors mounted on doors, windows, vents, and skylights.
4. A security alarm system is designed to detect intrusions. It protects against unauthorized entry and property damage.
5. The brain stem controls safety functions. It regulates essential involuntary functions such as breathing and heart rate.
6. The amygdala serves as the brain’s early alarm system for detecting threats. It quickly alerts us to potential threats unconsciously.
7. The four fundamentals of security are: confidentiality, integrity, availability, and non-repudiation.
8. Information security includes the components of confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Organizations must consider these factors in their cybersecurity strategy.
Questions and Answers
1. What part of the brain is the alarm system? The alarm system is controlled by the amygdala.
2. What are the three main parts of the security system? The three main parts are detectors, alarm control panel, and CMS.
3. What are the main parts of an alarm system? The main parts are perimeter protection, area protection, and spot protection.
4. What is a security system called? A security system is often referred to as a security alarm system.
5. What part of the brain controls safety? Safety functions are controlled by the brain stem.
6. Which part of the brain serves as the early alarm system for threat? The amygdala serves as the early alarm system for threats.
7. What are the four fundamentals of security? The four fundamentals are confidentiality, integrity, availability, and non-repudiation.
8. What is security and its components? Security includes the components of confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
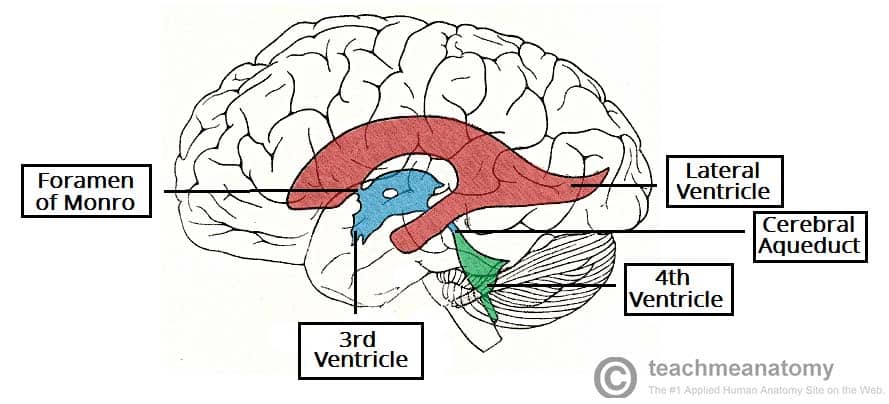
What part of the brain is the alarm system
amygdala
Your amygdala triggers your natural alarm system. When you experience a disturbing event, it sends a signal that causes a fear response. This makes sense when your alarm bells buzz at the right time and for the right reason: to keep you safe.
What are the three main parts of the security system
Alarm System is a security system consists of 3 parts alarm units. They are detectors, alarm control panel and CMS. … There are three main types of fire alarm monitoring systems: ionization, photoelectric, and combination alarms.
What are the main parts of an alarm system
A basic alarm system is divided into three layers: perimeter protection, area protection, and spot protection. Perimeter protection is the first line of defense to detect a potential intruder. Alarm sensors on the perimeter are typically mounted on doors, windows, vents, and skylights.
What is a security system called
A security alarm is a system designed to detect intrusions, such as unauthorized entry, into a building or other areas, such as a home or school. Security alarms protect against burglary (theft) or property damage, as well as against intruders.
CachedSimilar
What part of the brain controls safety
The brain stem controls the body's involuntary functions that are essential for survival, such as breathing and heart rate.
Which part of the brain serves as the early alarm system for threat
Bessel Van der Kolk calls the amygdala the “smoke detector” because it can be akin to a smoke detector sensing smoke or fire. This “alarm” system alerts us (swiftly and unconsciously) of whether an external stimulus is a threat.
What are the 4 fundamentals of security
There are four main principles of information security: confidentiality, integrity, availability, and non-repudiation.
What is security and its components
Therefore, the 3 components of information security—confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data—are factors every organization must consider when outlining their cybersecurity strategy.
What are the components of an electronic security system
Electronic Security SystemsPhysical Access Control Systems (PACS)Video Surveillance Systems (VSS) (sometimes known as CCTV)Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
What is the anatomy of a fire alarm system
In general terms, the main components of a fire alarm system are sensors. The sensors are connected to a central fire panel through cables that alert local emergency responders when an alarm is activated. The alarm can be activated manually or through smoke transmission, heat receptors, carbon monoxide detection, etc.
What’s another word for security system
What is another word for security system
| monitor | detector |
|---|---|
| recorder | scanner |
| CCTV | security camera |
What is a security man called
Industry terms for security personnel include: security guard, security officer, security agent, safety patrol, private police, company police, security enforcement officer, and public safety.
Which part of brain controls actions
Frontal lobe.
The largest lobe of the brain, located in the front of the head, the frontal lobe is involved in personality characteristics, decision-making and movement.
What part of the brain controls threats
The amygdala
The amygdala
Responding to threat involves many parts of the brain. But if any single brain structure can be seen as central to the process, it's the amygdala—an almond-shaped bundle of neurons buried deep in each medial temporal lobe, located just above the brain stem.
What are the 5 pillars of security
Understand the 5 PillarsPhysical Security. Physical Security relates to everything that is tangible in your organization.People Security. Humans typically present the greatest threat to an organisation's security, be it through human error or by malicious intent.Data Security.Infrastructure Security.Crisis Management.
What are the 5 C’s in security
Change, Compliance, Cost, Continuity, and Coverage; these are all fundamental considerations for an organization.
What are the 4 elements of security
An effective security system comprises of four elements: Protection, Detection, Verification & Reaction.
What are the 5 elements of security
It relies on five major elements: confidentiality, integrity, availability, authenticity, and non-repudiation.
What are the 4 components of network security
What Are the Essential Components of Network Security Firewalls, IPS, network access control (NAC), and security information and event management (SIEM) are the four most essential components of network security.
What are the three parts of an electronic system
An electric circuit has three parts: An energy source – like a battery or mains power. An energy receiver – like a lightbulb. An energy pathway – like a wire.
What is the most important part of a fire alarm system
Notification devices are arguably the most important parts of your fire alarm system. Notification devices can use audible, visible, tactile, textual and even smell-based stimuli to alert the people in your building of fire.
What are the two parts of fire protection system
Fire-protection systems fall into two main categories — passive fire protection and active fire protection.
What is security terminology
In contrast, security professional terminology describes defensive barrier devices, procedures, and policies. This is quite logical because hacking is an offensive activity centered on attackers and attack methodologies, whereas security is a defensive activity concerned with defensive barriers and procedures.
What is the professional term for security guard
Industry terms for security personnel include: security guard, security officer, security agent, safety patrol, private police, company police, security enforcement officer, and public safety.
Who is a head of security
A chief security officer (CSO) is an organization's most senior executive accountable for the development and oversight of policies and programs intended for the mitigation and/or reduction of compliance, operational, strategic, financial and reputational security risk strategies relating to the protection of people, …