Is Kaspersky good for ransomware?
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business, Kaspersky Small Office Security, and Kaspersky Internet Security have all demonstrated 100 percent effectiveness against ransomware attacks in grueling Advanced Threat Protection Test assessments by AV-TEST.
What is Kaspersky anti-ransomware?
Kaspersky Anti-Ransomware Tool for Home detects malicious applications or legitimate software that can be used to damage your data (adware and others) and automatically blocks suspicious activity. The application stores data areas modified by suspicious processes in the hidden and protected storage.
What does ransomware do?
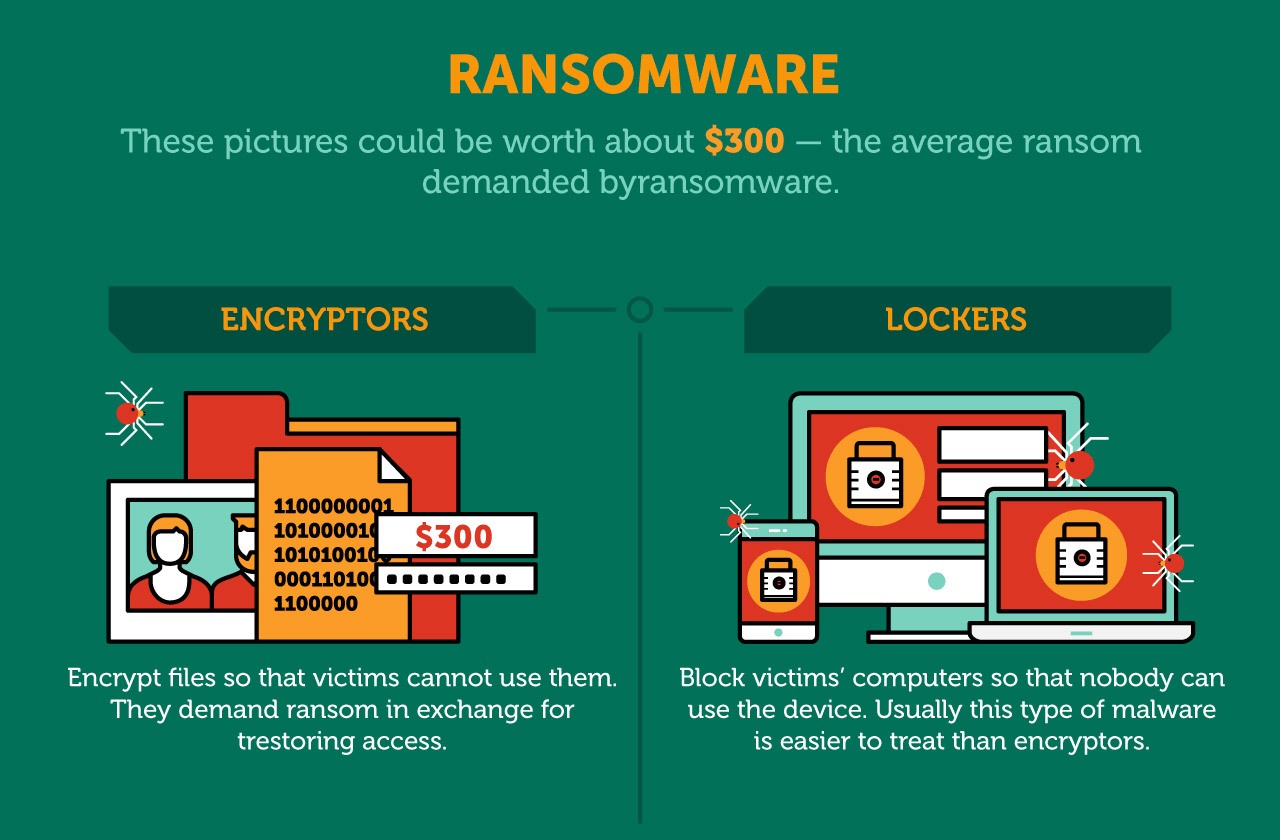
Ransomware is a type of malware which prevents you from accessing your device and the data stored on it, usually by encrypting your files. A criminal group will then demand a ransom in exchange for decryption.
What happens if you don’t pay ransomware?
In these cases, failure to comply with regulations or report a ransomware attack could land organization officials in prison or subject the business to hefty fines. Some countries have laws against ransom payments, making it illegal to comply with cybercriminals’ demands for funds.
Should I worry if I use Kaspersky?
Kaspersky’s malware scanner has been tested as recently as fall of 2022 by major testing labs. Such labs as AV-Comparatives and AV-Test showed that Kaspersky performed extremely well, capturing 100% of zero-day malware and 100% of widespread malware, with an excellent result of 0 false positives.
Why is Kaspersky a threat?
Why is Kaspersky banned The US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) banned Kaspersky because of concern that the company poses “an unacceptable risk to the national security of the United States.” The ban forbids companies from using FCC funds to purchase Kaspersky products.
Should you avoid Kaspersky?
Kaspersky’s malware scanner has been tested as recently as fall of 2022 by major testing labs. Such labs as AV-Comparatives and AV-Test showed that Kaspersky performed extremely well, capturing 100% of zero-day malware and 100% of widespread malware, with an excellent result of 0 false positives.
Should you stop using Kaspersky?
In April 2022, The German Federal Office for Information Security, known as BSI, urged the public to avoid using Kaspersky due to its ties to the Russian government. The BSI alleges that the firm could be implicated in hacking incidents related to Russia’s war against Ukraine.
Can you recover from ransomware?
Ransomware recovery typically takes a few days to a week, depending on the size and complexity of your company’s IT infrastructure. However, if you have a good backup and recovery plan in place, you can minimize the downtime and get your business back up and running as quickly as possible.
Can you get rid of ransomware?
Ransomware sometimes deletes itself after it has infected a system; other times, it stays on a device to infect other devices or files. Use antimalware/anti-ransomware. Most antimalware and anti-ransomware software can quarantine and remove the malicious software. Ask security professionals for help.
Should I worry about ransomware?
Ransomware is a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike. It can result in the loss of sensitive data, financial loss, and damage to reputation. It is crucial to take preventive measures such as using updated security software, regularly backing up data, and educating yourself about potential threats.
Is Kaspersky good for ransomware
Kaspersky Endpoint Security for Business, Kaspersky Small Office Security and Kaspersky Internet Security have all demonstrated 100 percent effectiveness against ransomware attacks in grueling Advanced Threat Protection Test assessments by AV-TEST.
What is Kaspersky anti-ransomware
Computer protection. Kaspersky Anti-Ransomware Tool for Home detects malicious applications or legitimate software that can be used to damage your data (adware and others) and automatically blocks suspicious activity. The application stores data areas modified by suspicious processes in the hidden and protected storage …
What does a ransomware do
Ransomware is a type of malware which prevents you from accessing your device and the data stored on it, usually by encrypting your files. A criminal group will then demand a ransom in exchange for decryption.
What happens if you don’t pay ransomware
In these cases, failure to comply with regulations or report a ransomware attack could land organization officials in prison or subject the business to hefty fines. Some countries have laws against ransom payments, making it illegal to comply with cybercriminals' demands for funds.
Should I worry if I use Kaspersky
Kaspersky's malware scanner has been tested as recently as fall of 2022 by major testing labs. Such labs as AV-Comparatives and AV-Test showed that Kaspersky performed extremely well, capturing 100% of zero-day malware and 100% of widespread malware, with an excellent result of 0 false positives.
Why is Kaspersky a threat
Why is Kaspersky banned The US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) banned Kaspersky because of concern that the company poses “an unacceptable risk to the national security of the United States.” The ban forbids companies from using FCC funds to purchase Kaspersky products.
Should you avoid Kaspersky
Kaspersky's malware scanner has been tested as recently as fall of 2022 by major testing labs. Such labs as AV-Comparatives and AV-Test showed that Kaspersky performed extremely well, capturing 100% of zero-day malware and 100% of widespread malware, with an excellent result of 0 false positives.
Should you stop using Kaspersky
In April 2022, The German Federal Office for Information Security, known as BSI, urged the public to avoid using Kaspersky due to its ties to the Russian government. The BSI alleges that the firm could be implicated in hacking incidents related to Russia's war against Ukraine.
Can you recover from ransomware
Ransomware recovery typically takes a few days to a week, depending on the size and complexity of your company's IT infrastructure. However, if you have a good backup and recovery plan in place, you can minimize the downtime and get your business back up and running as quickly as possible.
Can you get rid of ransomware
Ransomware sometimes deletes itself after it has infected a system; other times, it stays on a device to infect other devices or files. Use antimalware/anti-ransomware. Most antimalware and anti-ransomware software can quarantine and remove the malicious software. Ask security professionals for help.
Should I worry about ransomware
Ransomware is a legitimate risk for anyone with a computer and data they want keep accessible and secure.
Can ransomware be removed
Ransomware sometimes deletes itself after it has infected a system; other times, it stays on a device to infect other devices or files. Use antimalware/anti-ransomware. Most antimalware and anti-ransomware software can quarantine and remove the malicious software. Ask security professionals for help.
Can Kaspersky be trusted now
Kaspersky test results
AV-TEST puts all products through rigorous testing and is the most trusted source for independent testing for security products. Kaspersky regularly scores perfect or near perfect with each of its offerings when it comes to protection.
Should we delete Kaspersky
There are no solid reports of Kaspersky being a problem for individual users, but quite a number of security experts have urged those in government or sensitive industries like banking, energy and aerospace to refrain from using Kaspersky software.
Why did us ban Kaspersky
The administration ramped up its national security probe into Kaspersky Lab's antivirus software last year as fears grew about Russian cyberattacks after Moscow invaded Ukraine. U.S. regulators have already banned federal government use of Kaspersky software.
Is Kaspersky owned by Russian government
About Kaspersky
Kaspersky, one of the world's largest privately held cybersecurity companies, was founded in Russia in 1997 by Eugene Kaspersky.
Is Kaspersky good at removing malware
If left unchecked, malware can wreak havoc on your device, and you could be vulnerable to data theft. Fortunately, most malware is easy to remove with Kaspersky Anti-Virus.
What happens if you are attacked by ransomware
Ransomware is a malware designed to deny a user or organization access to files on their computer. By encrypting these files and demanding a ransom payment for the decryption key, cyberattackers place organizations in a position where paying the ransom is the easiest and cheapest way to regain access to their files.
Can ransomware destroy your computer
Exposure to other dangerous software: The purpose of some malware is to entice you to download even more dangerous software. Loss of information: Viruses might delete stored files or data, while ransomware may destroy your entire hard drive if specific demands aren't met.
Can ransomware steal your data
Yes. Some types of ransomware can steal all your personal data before encrypting your files.
Does ransomware damage your computer
Ransomware intentionally encrypts important files on your computer and causes great damage.
Does ransomware steal data or just lock it
Ransomware has been one of the most popular and successful malware types these days. With it, cybercriminals can successfully block access to your own data and devices, steal sensitive information, and earn a fortune by forcing you to pay a ransom.
Is Kaspersky blocked in the US
U.S. regulators have already banned federal government use of Kaspersky software.
Should people stop using Kaspersky
Plans and pricing. We don't recommend getting Kaspersky because of its ties to Russia's Federal Security Service (FSB). However, we strongly suggest looking into some alternatives, such as Bitdefender, TotalAV, or Norton.
Is Kaspersky owned by Russia
About Kaspersky
Kaspersky, one of the world's largest privately held cybersecurity companies, was founded in Russia in 1997 by Eugene Kaspersky.