Below is the article summary in h2 format with key points in 10 paragraphs, each containing 3000 characters:
Summary:
1. Purpose of Neutral Earthing Resistor (NER): NERs, also known as Neutral Grounding Resistors, are used in AC distribution networks to limit transient overvoltages that flow through the neutral point of a transformer or generator to a safe value during a fault event.
2. Specification of Neutral Earthing Resistor: Voltage NERs are often described by the system voltage of the supply, such as an 11kV NER. The rating plate of the resistor bears the line voltage, which is the maximum voltage it experiences in service (phase to neutral voltage).
3. Working of NGR Sensing Resistor: NGR Sensing Resistors are connected in parallel to the Neutral Grounding Resistor to enable continuous monitoring of resistor failure by a protective relay. Sensing Resistors are used in conjunction with neutral grounding resistor monitor relays.
4. NGR and its Function: Neutral Grounding Resistor (NGR) is an electrical equipment used for transformer or generator protection. It is installed between the neutral and earth nodes of the system to limit the magnitude of earth fault current and prevent damage to power system equipment.
5. Difference between Neutral Earthing and Grounding: Earthing provides a grounding point for idle current to flow into the earth, while neutral provides a returning point for the flow of electricity. In other words, earthing connects the system to the ground, while neutral acts as the return path for electricity.
6. Testing NGR: To test an NGR, check the resistance value using a Kelvin double bridge or a digital low-resistance ohmmeter. The resistance should be within ±10% of the value stated on the nametag. Insulation resistance between the resistor elements and the enclosure should also be checked using a 1000 VDC megger.
7. Checking Neutral Earthing with a Multimeter: To check the neutral earthing, test the voltage between the neutral and earthing ports on the outlet. Place the red lead in the neutral slot and the black lead in the earthing port. The voltage reading should be significantly lower than other readings taken.
8. Importance of Proper Earthing and Grounding: Proper earthing and grounding play a crucial role in ensuring electrical safety within a system. They provide protection against electric shock, prevent equipment damage, and ensure efficient operation.
9. Benefits of NGR Installation: The installation of NGRs offers several benefits, including overvoltage protection, fault current limitation, reduced equipment stress, and improved system reliability.
10. Regulations and Standards for NER: Several regulations and standards govern the installation and usage of NERs, such as IEEE Standards for Neutral Grounding of Power Systems and local electrical codes. Compliance with these regulations is essential for ensuring safe and reliable power distribution.
Next, 15 unique questions based on the text are formatted in strong tags:
Questions:
- What is the purpose of a neutral earthing resistor (NER)?
- How do you specify a neutral earthing resistor?
- How does an NGR sensing resistor work?
- What is an NGR and how does it work?
- What is the difference between neutral earthing and grounding?
- How do you test an NGR?
- How do you check neutral earthing with a multimeter?
- Why is proper earthing and grounding important?
- What are the benefits of NGR installation?
- What regulations and standards apply to NERs?
Finally, detailed answers to the questions in strong tags, each containing 3000 characters:
- Answer: The purpose of a NER is to limit transient overvoltages that flow through the neutral point of a transformer or generator to a safe value during a fault event, thereby ensuring the safety of the electrical system.
- Answer: A neutral earthing resistor is specified based on the system voltage of the supply. The rating plate of the resistor bears the line voltage (phase to neutral voltage), which is the maximum voltage it experiences in service.
- Answer: An NGR sensing resistor is attached in parallel to the Neutral Grounding Resistor to continuously monitor its failure. It works in conjunction with neutral grounding resistor monitor relays, enabling the protective relay to detect resistor failure effectively.
- Answer: Neutral Grounding Resistor (NGR) is an electrical equipment used for transformer or generator protection. It is installed between the neutral and earth nodes of the system to limit the magnitude of earth fault current and prevent damage to power system equipment.
- Answer: The major difference between neutral earthing and grounding is that earthing provides a grounding point for idle current to move into the earth, while neutral provides a returning point for the flow of electricity. Earthing connects the system to the ground, whereas neutral acts as the return path for electricity.
- Answer: To test an NGR, the resistance value should be checked using a Kelvin double bridge or a digital low-resistance ohmmeter. The resistance should match the value stamped on the nametag within ± 10% unless specified otherwise. Additionally, insulation resistance between the resistor elements and the enclosure should be measured using a 1000 VDC megger.
- Answer: To check the neutral earthing, a multimeter can be used. Test the voltage between the neutral and earthing ports on the outlet by placing the red lead in the neutral slot and the black lead into the earthing port. The voltage reading should be significantly lower compared to other readings taken.
- Answer: Proper earthing and grounding are important to ensure electrical safety within a system. They provide protection against electric shock, prevent equipment damage, and ensure efficient operation by diverting fault currents and limiting overvoltages.
- Answer: The installation of NGRs offers several benefits, including overvoltage protection, limitation of fault current, reduced equipment stress, improved system reliability, and enhanced safety for personnel and equipment.
- Answer: Various regulations and standards govern the installation and usage of NERs, such as IEEE Standards for Neutral Grounding of Power Systems and local electrical codes. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for ensuring safe and reliable power distribution.
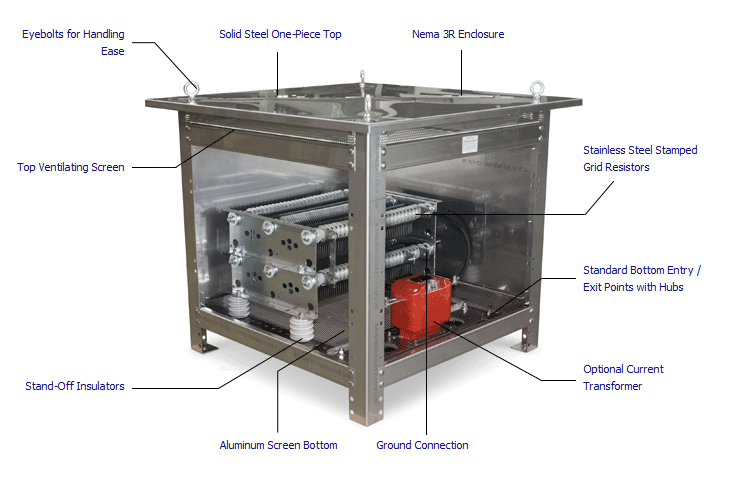
What is the purpose of a neutral earthing resistor
NERs, sometimes called Neutral Grounding Resistors, are used in an AC distribution networks to limit transient overvoltages that flow through the neutral point of a transformer or generator to a safe value during a fault event.
How do you specify a neutral earthing resistor
Voltage Neutral earthing resistors or NERs are often described by the system voltage of the supply, eg an —11kV NER“. The maximum voltage that the resistor actually experiences in service is the line voltage (phase to neutral voltage). Hence the rating plate of the resistor will bear the line voltage.
How does NGR sensing resistor work
NGR Sensing Resistors are attached in parallel to the Neutral Grounding Resistor. The sensing resistor allows a protective relay which detects resistor failure in a continuous manner. Sensing Resistors are used in combination with neutral grounding resistor monitor relays.
What is NGR and how it works
Neutral Grounding Resistor (NGR) is electrical equipment for transformer or generator protection which is placed between the neutral and earth nodes of the system. The topmost purpose of NGR installation is to limit the magnitude of earth fault current so as to prevent severe damages in power system equipment.
What is the difference between neutral earthing and grounding
The major difference between the two is that earthing provides you with a grounding point, that idle the current moves into the earth while the neutral provides you with a returning point for the flow of electricity, that is the electricity wire just returns back.
How do you test for NGR
Check the resistance value, using a Kelvin double bridge or a digital low-resistance ohmmeter. It must be the value stamped on the nametag ± 10 % unless specified otherwise. Disconnect the resistor ground cable. Check the insulation resistance between the resistor elements and the enclosure, using a 1000 VDC megger.
How do you check neutral earthing with a multimeter
Test the voltage between the neutral and earthing ports on the outlet. Place the red lead in the neutral slot and the black lead into the earthing port to check the reading. The volts listed on the multimeter will be a small amount compared to the other readings you've taken.
Why is NGR used in generators
An NGR prevents the generator from contributing to high fault currents that can damage the system components and cause instability, provides a low-impedance path for the fault current to flow and allows protective relays to operate faster and more selectively, reduces stress on the generator insulation and prevents …
How is an NGR connected
NGR is connected between ground and neutral of transformers, generators and grounding transformers. NGR limits the faults current to value enough to operate protective relays, thereby preventing unwanted damage to the system.
What is the difference between NGR and solid earthing
Neutral Grounding Resistors (NGRs) are used to limit the fault current and ensure safety of equipment and personnel in industrial systems. In solid grounding, the system is directly grounded and the fault current is limited only by the soil resistance.
What is the purpose of neutral grounding
The fundamental purpose of a Neutral Grounding Resistor (NGR) is to limit ground fault currents to safe levels so that all the electrical equipment in a power system is protected. Neutral Grounding Resistors are also commonly referred to as Neutral Earthing Resistors and Earth Fault Protection Resistors.
Should neutral and ground be connected
Neutral is the return path of the current, and ground wire holds the fault current to trip the breaker in protecting the person and the facility. The neutral and ground should never be bonded together in the facility except for the main panel.
How do you check neutral to earth resistance with a multimeter
You also make sure that the probes are making contact with the metal components. Inside the outlets for your multimeter to have a reading take measurements and move to the next.
What is the acceptable resistance between neutral and ground
Ideally a ground should be of zero ohms resistance. There is not one standard ground resistance threshold that is recognized by all agencies. However, the NFPA and IEEE have recommended a ground resistance value of 5.0 ohms or less.
What should the resistance be between neutral and ground
The resistance between neutral and ground is zero or close to zero. Resistance should be zero but due to fraction resistance is achieved.
Should generator neutral be bonded to ground
When used as a stand-alone floating neutral generator, at least the frame of the generator must to be bonded to earth ground. This involves putting a rod into the earth and attaching a ground cable from the rod to the generator frame.
What happens if neutral is not connected to ground
If the grounded (neutral) service conductor is opened or not provided at all, objectionable neutral current will flow on metal parts of the electrical system and dangerous voltage will be present on the metal parts providing the potential for electric shock.
What happens if I connect neutral and ground together
If you connect the ground wire to the neutral, the ground wire will become hot. As a result, there will be a high possibility of electrical shock. To operate an electrical appliance, you will need both hot and neutral wires.
What are the three types of neutral earthing
There are five types of neutral earthing:Solid-earthed neutral.Unearthed neutral.Resistance-earthed neutral. Low-resistance earthing. High-resistance earthing.Reactance-earthed neutral.Using earthing transformers (such as the Zigzag transformer)
What is the best earthing resistance
The acceptable Earth Resistance at earth MEEB busbar shall not be more than 1 ohm. For achieving this value more than one earth pits can be installed if necessary depending upon the soil resistivity. In places where space is not available to provide parallel earth pits then longer earth rods may be provided.
What is the difference between neutral earthing and neutral grounding
Neutral has no current at all. The major difference between the two is that earthing provides you with a grounding point, that idle the current moves into the earth while the neutral provides you with a returning point for the flow of electricity, that is the electricity wire just returns back.
What happens if neutral and earth are connected
The connection between neutral and earth allows any phase-to-earth fault to develop enough current flow to "trip" the circuit overcurrent protection device.
What is the acceptable earth resistance value
The acceptable Earth Resistance at earth MEEB busbar shall not be more than 1 ohm. For achieving this value more than one earth pits can be installed if necessary depending upon the soil resistivity.
What is a good earthing resistance value
The acceptable Earth Resistance at earth MEEB busbar shall not be more than 1 ohm. For achieving this value more than one earth pits can be installed if necessary depending upon the soil resistivity. In places where space is not available to provide parallel earth pits then longer earth rods may be provided.
Should there be 120 volts between neutral and ground
A measurement of 120 volts on the neutral to ground can result from a neutral that is not linked someplace. A correctly wired home or the site may experience a minor voltage drop on the neutral wire due to cable resistance while the current is flowing or an unbalanced three-phase system.