a key. a key for winding a clock. : a means of gaining or preventing entrance, possession, or control. : an instrumental or deciding factor.[/wpremark]
How do you use an identification key in biology Using an identification key in biology involves following a series of choices based on observable traits of the organism being identified. The key consists of a series of statements or questions, each with two choices. By selecting the choices that most closely match the traits observed, the user can narrow down the options and eventually arrive at the correct identification of the organism.
What are the benefits of using a key in biology Using a key in biology has several benefits. First, it provides a systematic approach to identifying organisms based on their observable traits. This allows scientists to categorize and classify organisms accurately. Second, it allows for the discovery of new species by identifying organisms that do not match any known species. Lastly, keys can be used as teaching tools to help students learn about the diversity of living organisms.
How accurate are identification keys in biology Identification keys in biology are generally accurate, but their accuracy depends on the quality of the key and the expertise of the user. Keys that are well-designed and based on extensive research and observation are more likely to yield accurate identifications. However, errors can occur if the key is outdated or if the user misinterprets or misapplies the key’s instructions. Therefore, it is important for users to exercise caution and verify their identifications using additional sources and expert consultation if necessary.
Can keys in biology be used to identify any type of organism Identification keys in biology can be used to identify a wide range of organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. However, the design and content of the key may vary depending on the group of organisms being identified. Keys for plants, for example, may focus on characteristics such as leaf shape, flower structure, and fruit type, while keys for animals may emphasize traits like body size, coloration, and habitat preferences. Therefore, it is important to select a key that is appropriate for the specific group of organisms being studied.
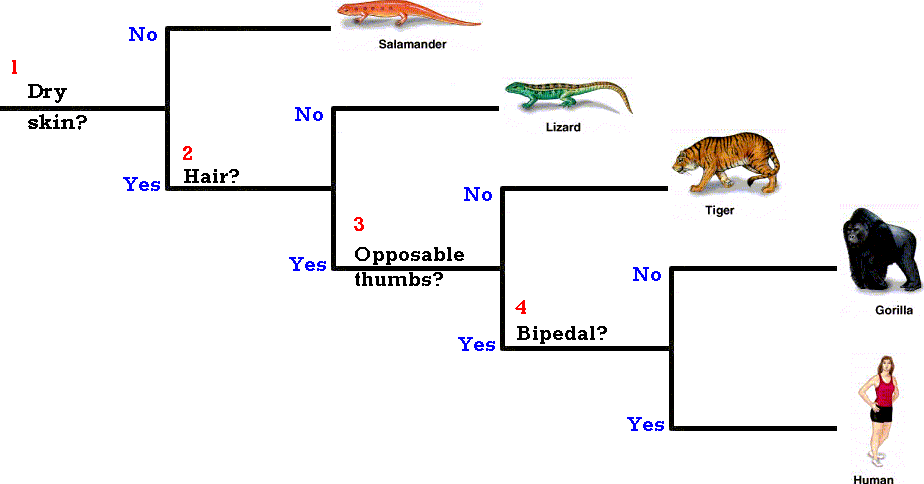
What is the purpose of a dichotomous key The purpose of a dichotomous key is to enable users to identify an organism by systematically eliminating choices based on observable traits. By presenting two contrasting options at each step, the key helps the user narrow down the possibilities and eventually arrive at the correct identification. The use of a dichotomous key ensures a logical and consistent approach to identification, regardless of the user’s prior knowledge or experience with the organisms being studied.
Are keys in biology used only for identification purposes While identification is the primary purpose of keys in biology, they can also serve other purposes. Keys can provide valuable information about the characteristics and traits of different organisms, allowing for the comparison and classification of species. Additionally, keys can be used in ecological studies to identify the presence of certain organisms in a particular habitat. Overall, keys play a crucial role in understanding and documenting the diversity of life on Earth.
Can identification keys be subjective Identification keys in biology are designed to minimize subjectivity and provide an objective approach to identifying organisms. However, some degree of subjectivity can still arise, especially when certain traits or characteristics are open to interpretation. Additionally, user error or bias can influence the accuracy of identifications. To mitigate subjectivity, keys are often based on well-defined and measurable traits, and multiple diagnostic features are typically included to increase reliability. Additionally, expert consultation and further analysis can be used to confirm identifications and reduce subjective errors.
In biology, an identification key, taxonomic key, or biological key is a printed or computer-aided device that aids the identification of biological entities, such as plants, animals, fossils, microorganisms, and pollen grains.
CachedSimilar
What is an example of a key in biology
EXAMPLE OF A TAXONOMIC KEY
This is a simple taxonomic key allowing the user to identify the following common grocery store fruits: apple, banana, orange, peach, tomato, and watermelon. To use the key, pick one of these as your unknown, then read both halves of the first couplet. Which half better describes your fruit
What is a key in science
A taxonomic key is a simple tool used to identify a specific object. A taxonomic key is one of the most useful tools available to scientists trying to identify an unknown organism. Systematists rely on keys to help identify known organisms and determine whether they have discovered a new organism entirely.
What are the 2 types of keys in biology
A key is a device, which when properly constructed and used, enables a user to identify an organism. There are three types of keys that we will discuss; (a) dichotomous; (b) polyclave (also called multiple access or synoptic); and (c) probability.
Cached
What’s a key
: a usually metal instrument by which the bolt of a lock is turned. : any of various devices having the form or function of such a key. a key for winding a clock. : a means of gaining or preventing entrance, possession, or control. : an instrumental or deciding factor.
Why do biologists use a key
Objective. A dichotomous key is an important scientific tool, used to identify different organisms, based the organism's observable traits. Dichotomous keys consist of a series of statements with two choices in each step that will lead users to the correct identification.
How do you make a biology key
How to Make a Dichotomous KeyStep 1: List down the characteristics.Step 2: Organize the characteristics in order.Step 3: Divide the specimens.Step 4: Divide the specimen even further.Step 5: Draw a dichotomous key diagram.Step 6: Test it out.
What’s an key
: a usually metal instrument by which the bolt of a lock is turned. : any of various devices having the form or function of such a key. a key for winding a clock. : a means of gaining or preventing entrance, possession, or control. : an instrumental or deciding factor.
What you meant by a key
A key is a specially shaped piece of metal that you place in a lock and turn in order to open or lock a door, or to start or stop the engine of a vehicle.
How many keys are there in biology
There are three main types of biological key.
What are keys in classification
A key is a set of questions about the characteristics of living things. You can use a key to identify a living thing or decide which group it belongs to by answering the questions.
What is a key used for
A key is a device that is used to operate a lock (to lock or unlock it). A typical key is a small piece of metal consisting of two parts: the bit or blade, which slides into the keyway of the lock and distinguishes between different keys, and the bow, which is left protruding so that torque can be applied by the user.
What is key in biology class 11
A key is responsible for creating a framework that can be used to sort a large amount of data. This allows the user to identify unrelated species that have no biological similarities. A key comes with a lot of couplets. Each couplet has two traits that are diametrically opposed.
What is the purpose of a key
A key is a device that is used to operate a lock (to lock or unlock it). A typical key is a small piece of metal consisting of two parts: the bit or blade, which slides into the keyway of the lock and distinguishes between different keys, and the bow, which is left protruding so that torque can be applied by the user.
How do you use a biological key
You can clearly see in photograph a that the bird has a very curved beak. So we write hornbill for a we've identified the first one.
What is a key and what is its function
What is Key A key is a machine element which is used to connect a shaft to other machine elements like Gears, Pullies, Couplings, Sprockets or Flywheels. Its primary function is to prevent relative motion between connected parts.
What is a key in drugs
Door/Key. A kilo of drugs. Flippin Chickens. A 'chicken' is another word for a kilo of cocaine.
What is key and lock biology
Lock-and-key model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction suggesting that the enzyme and the substrate possess specific complementary geometric shapes that fit exactly into one another. Enzymes are highly specific. They must bind to a specific substrate before they can catalyze a chemical reaction.
How can a key be used to identify organisms
To classify organisms, scientists will often use a biological key or a dichotomous key. A dichotomous key is a listing of specific traits, primarily structural, that allows an organism to be sorted into one of two categories. By using a dichotomous key unknown organisms can be identified.
What are keys in data structure
A key in DBMS is an attribute or a set of attributes that help to uniquely identify a tuple (or row) in a relation (or table). Keys are also used to establish relationships between the different tables and columns of a relational database. Individual values in a key are called key values.
What makes it a key
A key is a small, low-lying coral island. Like all coral islands, keys are the remnants of ancient coral reefs, and many keys are still ringed by healthy reef ecosystems. Over time, the top of a coral reef is exposed to the surface.
What is a key to species identification
Species identification is often done with the aid of traditional dichotomous keys. This printed material is based on one's decision between two alternatives, which is followed by another pair of alternatives until the final species name is reached.
Why is function key used
Keys with an Fn key or F Lock provide two sets of commands for many keys. This includes the top row of standard function keys (F1–F12). Standard commands are labeled on the front of the keys (such as F3). Alternate commands are labeled on top of the keys (such as Redo).
What class of drug is key
Ketamine
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Any |
| Drug class | NMDA receptor antagonists; General anesthetics; Dissociative hallucinogens; Analgesics; Antidepressants |
| ATC code | N01AX03 (WHO) |
| Legal status |
What does lock and key mean enzyme
Lock and key hypothesis
Enzymes are folded into complex 3D shapes that allow smaller molecules to fit into them. The place where these molecules fit is called the active site . In the lock and key hypothesis , the shape of the active site matches the shape of its substrate molecules. This makes enzymes highly specific.