Summary of the article:
1. What qualifies as Personally Identifiable Information (PII)?
PII is defined as information that directly identifies an individual or by which an agency intends to identify specific individuals in conjunction with other data elements. Examples include names, addresses, social security numbers, telephone numbers, and email addresses.
2. What are examples of PII as per GDPR guidelines?
Examples of PII under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) include names, addresses, financial information, login IDs, biometric identifiers, video footage, geographic location data, and customer loyalty histories.
3. What are 5 examples of PII?
Examples of PII include social security numbers (SSN), passport numbers, driver’s license numbers, taxpayer identification numbers, and financial account numbers.
4. What is not considered PII (Personally Identifiable Information)?
Non-PII refers to data that cannot be used on its own to trace or identify a person. Examples of non-PII include aggregated statistics on the use of a product or service.
5. What does PII not include?
Non-PII includes partially or fully masked IP addresses and data that cannot be used on its own to trace or identify a person. Examples include aggregated statistics on product/service use.
6. What is not considered as PII?
Information such as business phone numbers and details like race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles are typically not considered PII.
7. Which 5 types of information are examples of PII?
Examples of PII include full name, home address, email address, social security number, passport number, driver’s license number, credit card numbers, and date of birth.
8. What are 4 examples of PII?
Examples of PII include social security numbers (SSN), passport numbers, driver’s license numbers, taxpayer identification numbers, patient identification numbers, financial account numbers, and credit card numbers.
Questions:
1. What qualifies as PII?
PII refers to information that directly identifies an individual or is used to identify specific individuals in combination with other data elements.
2. What are examples of PII under GDPR guidelines?
Examples of PII as per GDPR guidelines include names, addresses, financial information, login IDs, biometric identifiers, video footage, geographic location data, and customer loyalty histories.
3. What are some common types of PII?
Common types of PII include social security numbers, passport numbers, driver’s license numbers, taxpayer identification numbers, and credit card numbers.
4. What is the difference between PII and non-PII?
PII refers to sensitive data that can be used to identify an individual, while non-PII cannot be used on its own to trace or identify a person.
5. What are examples of non-PII?
Examples of non-PII include aggregated statistics on product or service usage and partially or fully masked IP addresses.
6. Can business phone numbers be considered PII?
No, business phone numbers are typically not considered PII as they do not directly identify an individual.
7. What are the consequences of mishandling PII?
Mishandling PII can lead to data breaches, identity theft, and legal repercussions, including fines and penalties.
8. How can individuals protect their PII?
Individuals can protect their PII by using strong, unique passwords, being cautious of sharing personal information online, regularly reviewing privacy settings, and staying updated on privacy policies.
9. What steps can organizations take to protect PII?
Organizations can protect PII by implementing strong security measures, encrypting sensitive data, conducting regular risk assessments, providing cybersecurity training to employees, and following data protection regulations.
10. What are the key principles of handling PII?
The key principles of handling PII are consent, purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity and confidentiality, accountability, and transparency.
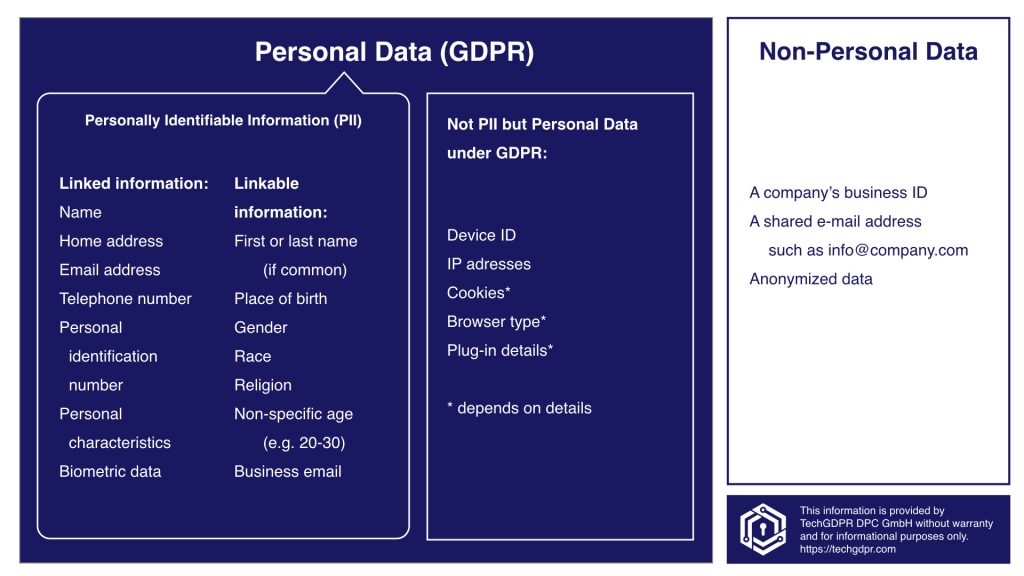
What qualifies as PII
Further, PII is defined as information: (i) that directly identifies an individual (e.g., name, address, social security number or other identifying number or code, telephone number, email address, etc.) or (ii) by which an agency intends to identify specific individuals in conjunction with other data elements, i.e., …
CachedSimilar
What are examples of PII as per GDPR guidelines
What Is Considered PII Under the GDPRNames.Addresses.Financial information.Login IDs.Biometric identifiers.Video footage.Geographic location data.Customer loyalty histories.
Cached
What are 5 examples of PII
Personal identification numbers: social security number (SSN), passport number, driver's license number, taxpayer identification number, patient identification number, financial account number, or credit card number.
What is not PII personally identifiable information
Non-personally identifiable information (non-PII) is data that cannot be used on its own to trace, or identify a person. Examples of non-PII include, but are not limited to: Aggregated statistics on the use of product / service.
What does PII not include
Non-personally identifiable information (non-PII) is data that cannot be used on its own to trace, or identify a person. Examples of non-PII include, but are not limited to: Aggregated statistics on the use of product / service. Partially or fully masked IP addresses.
What is not considered as PII
PII, or personally identifiable information, is sensitive data that could be used to identify, contact, or locate an individual. What are some examples of non-PII Info such as business phone numbers and race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles are typically not considered PII.
Which 5 types of information are examples of PII
What pieces of information are considered PIIFull name.Home address.Email address.Social security number.Passport number.Driver's license number.Credit card numbers.Date of birth.
What are 4 examples of PII
Personal identification numbers: social security number (SSN), passport number, driver's license number, taxpayer identification number, patient identification number, financial account number, or credit card number.
Which four examples of information qualify as PII
Name: full name, maiden name, mother's maiden name, or alias. Personal identification numbers: social security number (SSN), passport number, driver's license number, taxpayer identification number, patient identification number, financial account number, or credit card number.
What is the difference between PII and GDPR
PII has a limited scope of data which includes: name, address, birth date, Social Security numbers and banking information. Whereas, personal information in the context of the GDPR also references data such as: photographs, social media posts, preferences and location as personal.
What information is not considered PII
Info such as business phone numbers and race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles are typically not considered PII. But they should still be treated as sensitive, linkable info because they could identify an individual when combined with other data.
Which is not Categorised as PII data
Non-PII data typically includes data collected by browsers and servers using cookies. Device type, browser type, plugin details, language preference, time zone, screen size are few examples of non PII data.
What is not considered PII
PII, or personally identifiable information, is sensitive data that could be used to identify, contact, or locate an individual. What are some examples of non-PII Info such as business phone numbers and race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles are typically not considered PII.
Is a photo considered PII under GDPR
Is a photo considered PII The GDPR does not explicitly include a photograph as part of the definition of PII. However, any information that can be used to identify an individual, such as a facial image, may be considered personal data depending on its context and purpose.
Which of the following is not an example of PII
Info such as business phone numbers and race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles are typically not considered PII.
What is an example of a PII and a non-PII
PII, or personally identifiable information, is sensitive data that could be used to identify, contact, or locate an individual. What are some examples of non-PII Info such as business phone numbers and race, religion, gender, workplace, and job titles are typically not considered PII.