Summary of the Article
1. Major roads, also known as arterials, are expected to carry large volumes of traffic and can be divided into major and minor arterials, as well as rural and urban arterials.
2. There are three main classifications of roadways: arterial, collector, and local roads. These classifications depend on the character of the traffic and the degree of land access they allow.
3. In the United States, highways are categorized into four different types of systems: Interstate Highways, U.S. Highways, state highways, and county highways. These highways are distinguished by route numbers or letters.
4. The difference between major and minor arterial roads lies in their size and functionality. Major arterials typically have four or more lanes with speeds exceeding 45 MPH and are less pedestrian and bicycle-friendly. Minor arterials serve smaller geographic areas.
5. There are two types of roads based on topography: hilly roads and plain roads.
6. In America, a main road is commonly referred to as a highway. Highways encompass both major roads and other public roads or tracks.
7. The four major functional classifications of highways are Interstates, Other Arterials, Collectors, and Local roads. Each classification offers varying levels of mobility and land access.
8. Bituminous roads are the most preferred type of road.
Questions and Detailed Answers
1. What are major roads called?
Major roads are called arterials. They are expected to carry large volumes of traffic and can be divided into major and minor arterials, as well as rural and urban arterials.
2. What are the three main classifications of roadways?
The three main classifications of roadways are arterial, collector, and local roads. They are grouped based on the character of the traffic (local or long distance) and the degree of land access they provide.
3. What are the different road classifications in the US?
In the United States, highways are categorized into four different types of systems: Interstate Highways, U.S. Highways, state highways, and county highways. These highways are identified by route numbers or letters displayed along the route.
4. What is the difference between a major and minor arterial road?
Major arterials typically have four or more lanes with speeds exceeding 45 MPH, making them inhospitable and dangerous for pedestrians and bicyclists. On the other hand, minor arterials serve smaller geographic areas but function similarly.
5. How many types of roads are there?
Roads are classified into two types based on topography: hilly roads and plain roads.
6. What is a main road called in America?
In America, a main road is commonly referred to as a highway. Highways include major roads as well as other public roads and tracks.
7. What are the four functional classifications of highways?
The four major functional classifications of highways are Interstates, Other Arterials, Collectors, and Local roads. Each classification offers different levels of mobility and land access.
8. Which type of road is most preferred?
The most preferred type of road is bituminous roads.
What are major roads called
Arterials. Arterials are major through roads that are expected to carry large volumes of traffic. Arterials are often divided into major and minor arterials, and rural and urban arterials.
Cached
What are the three main classifications of roadways
There are three highway functional classifications: arterial, collector, and local roads. All streets and highways are grouped into one of these classes, depending on the character of the traffic (i.e., local or long distance) and the degree of land access that they allow.
What are the different road classifications in the US
Highways are split into at least four different types of systems in the United States: Interstate Highways, U.S. Highways, state highways, and county highways. Highways are generally organized by a route number or letter. These designations are generally displayed along the route by means of a highway shield.
What is the difference between a major and minor arterial road
Typically with four or more lanes and speeds exceeding 45 MPH, Major Arterials are inhospitable and dangerous for pedestrians and bicyclists. Minor Arterial : Although similar in functionality, Minor Arterials serve smaller geographic areas than Major Arterials.
Cached
How many types are there in road
Roads are classified into two types considering topography they are Hilly roads and Plain roads.
What is a main road called in America
highway
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks. In the United States, it is used as an equivalent term to controlled-access highway, or a translation for autobahn, autoroute, etc.
What are the four functional classifications of highways
The following photos and information illustrate the four major road function classifications: Interstates, Other Arterials, Collectors, and Local roads. The amount of mobility and land access offered by these road types differs greatly.
Which of the following types of roads are most
The most preferred type of road is bituminous roads.
How do you identify an arterial road
For the everyday motorist, the easiest way to identify an arterial road is by speed limits and intersections. Anything below 45 MPH is most likely a local or collector road and anything between 45-55 MPH that eventually leads to a freeway is most likely an arterial road.
What is a major arterial road
These arterial roads provide the highest level of mobility and the highest speeds over the longest uninterrupted distance. Interstates nationwide usually have posted speeds between 55 and 75 mi/h.
What are small roads called
byway. noun. a quiet minor road that is not used by many cars or people.
What is the most common road name
Trees, numbers, and presidents are the most popular names for streets, which is understandable.
What is the oldest road in America
the King’s Highway
The construction of the oldest road in America took place between 1650-1735, decades before the United States became a country. So with absolutely no doubt or question, the King's Highway is the oldest road in America. The road was was 1,300 miles long and connected Charleston, South Carolina, to Boston, Massachusetts.
What is the national functional classification of roads
The functional classification of a road is the class or group of roads to which the road belongs. There are three main functional classes as defined by the United States Federal Highway Administration: arterial, collector, and local.
Which type roads are most preferred for highway
In conclusion, bituminous roads are the most preferred type of roads for highways due to their smooth surface, durability, easy maintenance, and cost-effectiveness. Other types of roads such as cement concrete roads, gravel roads, and unpaved surfaces are not suitable for highways due to various reasons.
What is the difference between an arterial road and a local road
Collector streets serve to collect and distribute traffic between local streets and arterial roads. Arterial roads (with the expressway system) provide the major corridors for traffic (including surface transit) movement. Arterial roads are also important for pedestrians and cyclists.
What is the difference between an arterial road and a collector road
Collectors are major and minor roads that connect local roads and streets with arterials. Collectors provide less mobility than arterials at lower speeds and for shorter distances. They balance mobility with land access. The posted speed limit on collectors is usually between 35 and 55 mi/h.
What is the difference between collector and arterial roads
Collectors are major and minor roads that connect local roads and streets with arterials. Collectors provide less mobility than arterials at lower speeds and for shorter distances. They balance mobility with land access. The posted speed limit on collectors is usually between 35 and 55 mi/h.
What is the difference between arterial and local roads
Arterials provide longer through travel between major trip generators (larger cities, recreational areas, etc.); collector roads collect traffic from the local roads and also connect smaller cities and towns with each other and to the arterials; and local roads provide access to private property or low volume public …
What is a very narrow street called
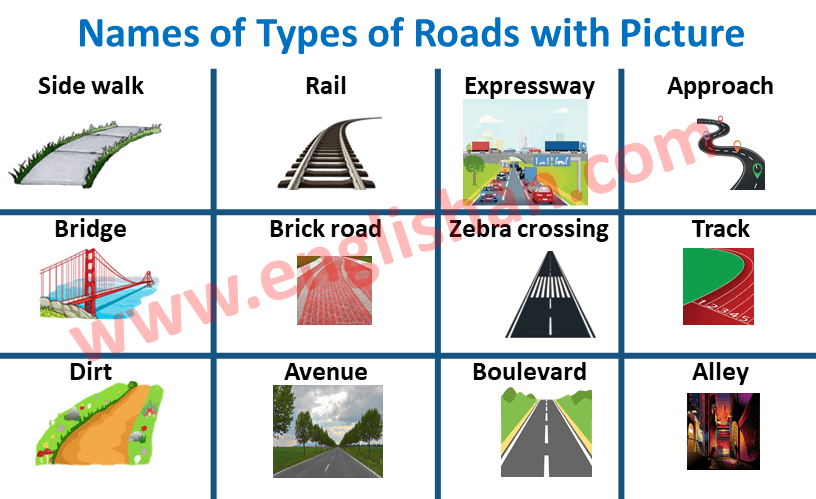
An alley or alleyway is a narrow lane, path, or passageway, often reserved for pedestrians, which usually runs between, behind, or within buildings in the older parts of towns and cities.
What are rough roads called
A dirt road or track is a type of unpaved road not paved with asphalt, concrete, brick, or stone; made from the native material of the land surface through which it passes, known to highway engineers as subgrade material.
What is the most popular road name in America
Even with the house number aside, Main Street is the most popular residential street name to live on, followed by numbered streets. Overall, researchers say these are the top 10 most common street names in the U.S.: Main Street. 2nd Street.
What is a main road in a city called
arterial road. a major or main route. beltway, bypass, ring road, ringway. a highway that encircles an urban area so that traffic does not have to pass through the center.
What is the most famous road in America
Route 66
It doesn't get any more famous than Route 66. The 'Historic' Route 66, constructed in 1926. “The Mother Road.” Chances are this famous highway is ringing some bells. Route 66 begins in Chicago and goes through SIX states (Santa Monica, California.
What is the longest straightest road in America
North Dakota claims its Highway 46 is the longest straight road in the US and Canada. Slight bends aside, the motorway boasts a 31-mile dead straight stretch from Gackle to Beaver Greek. However, the aforementioned Bonneville Salt Flat road is meant to be longer, at 35 miles.