Summary of the Article
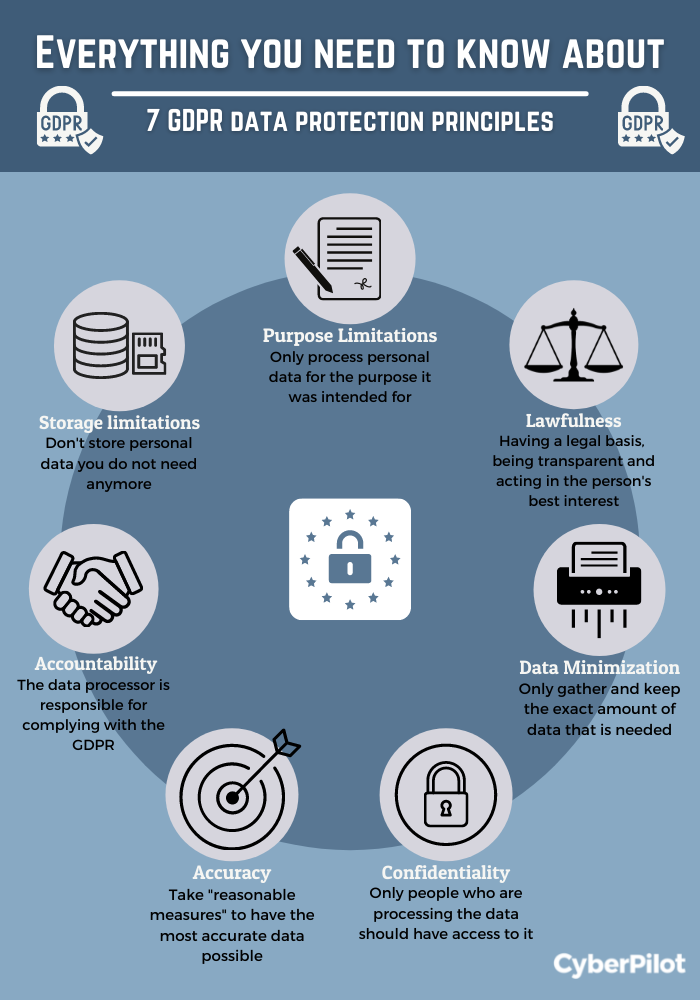
The Data Protection Act and GDPR enforce certain principles to ensure fair and lawful use of personal data. These principles include transparency, specific purposes for data use, minimum data requirements, accuracy, data retention time limits, the right to be forgotten, ensuring data security, and accountability. Data governance under GDPR is based on seven principles, including lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity, confidentiality, and accountability.
The third principle of the Data Protection Act requires that personal data processing must be adequate, relevant, and not excessive. This means that data should be limited to what is necessary for the intended purpose. The Act also includes the right to have data erased, stop or restrict the processing of data, data portability, and the right to object to certain processing activities.
The golden rule of data protection is honesty and transparency. Companies must be honest about the data collected, used, bought, or sold, and they need to clearly communicate their data privacy practices to consumers. The principles of data protection cover aspects like lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity, confidentiality, and accountability.
Principle 7 of the Data Protection Act 1998 states that appropriate technical and organizational measures should be taken to protect personal data against unauthorized or unlawful processing, accidental loss, destruction, or damage.
The principle of storage limitation means that personal data should not be kept longer than necessary for the purposes it was collected. It ensures that organizations adhere to a specific retention period and do not store data indefinitely.
Questions and Answers
- What are the 8 rules of the Data Protection Act?
- Fair and lawful use
- Transparency
- Specific purposes for data use
- Minimum data requirements
- Need for accuracy
- Data retention time limits
- The right to be forgotten
- Ensuring data security
- What are the seven principles of data governance as defined by GDPR?
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
- Purpose limitation
- Data minimization
- Accuracy
- Storage limitation
- Integrity and confidentiality (security)
- Accountability
- What is principle 3 of the Data Protection Act?
- What are the three requirements of the Data Protection Act?
- Right to have data erased
- Ability to stop or restrict the processing of data
- Data portability, allowing individuals to obtain and reuse their data for different services
- Right to object to certain data processing activities in specific circumstances
- What is the golden rule of data protection?
- Are there 10 principles of data protection?
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
- Specific purposes for data use
- Minimum data requirements
- Need for accuracy
- Data retention time limits
- The right to be forgotten
- Ensuring data security
- Accountability
- What is principle 7 of the Data Protection Act 1998?
- What does the principle of storage limitation cover?
The eight principles of the Data Protection Act are:
The seven principles of data governance under GDPR are:
Principle 3 of the Data Protection Act requires that personal data processing should be adequate, relevant, and not excessive. This means that data should be limited to what is necessary for the purpose it is being processed. Accuracy is also a key element of this principle.
The three requirements of the Data Protection Act are:
The golden rule of data protection is honesty and transparency. Companies must be honest about the data they collect, use, buy, or sell. They should communicate their data privacy practices clearly to all consumers, regardless of their level of tech-savviness.
No, there are eight principles of data protection:
Principle 7 of the Data Protection Act 1998 states that appropriate technical and organizational measures should be implemented to protect personal data against unauthorized or unlawful processing, accidental loss, destruction, or damage.
The principle of storage limitation ensures that personal data is not retained for longer than necessary for the purposes it was collected. It requires organizations to adhere to a specific retention period and avoid storing data indefinitely to protect individuals’ privacy.
What are the 8 rules of the Data Protection Act
What Are the Eight Principles of the Data Protection ActFair and Lawful Use, Transparency. The principle of this first clause is simple.Specific for Intended Purpose.Minimum Data Requirement.Need for Accuracy.Data Retention Time Limit.The right to be forgotten.Ensuring Data Security.Accountability.
What are the seven principles of data governance as defined by GDPR
According to the ICO's website, The GDPR was developed based upon seven principles: 1) lawfulness, fairness and transparency; 2) purpose limitation; 3) data minimization; 4) accuracy; 5) storage limitation; 6) integrity and confidentiality (security); and 7) accountability.
Cached
What is principle 3 of data protection act
The third principle requires that the personal data you are processing is adequate, relevant and not excessive. This means the data must be limited to what is necessary for the purpose(s) you are processing it. The fourth data protection principle is about accuracy.
What are the three requirements of the Data Protection Act
have data erased. stop or restrict the processing of your data. data portability (allowing you to get and reuse your data for different services) object to how your data is processed in certain circumstances.
What is the golden rule of data protection
HONESTY – Companies must be honest about the data collected, used, bought, or sold. TRANSPARENCY – Companies need to stop burying data collection policies deep within lengthy legal documents and instead be straightforward with all consumers (regardless of their level of tech-savviness) regarding data privacy practices.
Are there 10 principles of data protection
FormatLawfulness, fairness and transparency.Purpose limitation.Data minimisation.Accuracy.Storage limitation.Integrity and confidentiality (security)Accountability principle.
What is principle 7 of the data protection Act 1998
7Appropriate technical and organisational measures shall be taken against unauthorised or unlawful processing of personal data and against accidental loss or destruction of, or damage to, personal data.
What does storage limitation in the 7 key data protection principles cover
Under the “storage limitation” principle, you must not keep personal data for longer than you need it. You should tell people how long you'll keep each type of personal data you collect. You might store personal data for: A specific time period (e.g. one year).
What is principle 1 of data protection
You must use personal data in a way that is fair. This means you must not process the data in a way that is unduly detrimental, unexpected or misleading to the individuals concerned. You must be clear, open and honest with people from the start about how you will use their personal data.
What is the 6 principle of the data protection Act
The data protection principles that would be impacted include 1 – lawful, fair and transparent; 2 – limited for its purpose and 6 – integrity and confidentiality. Data that is collected for deceptive or misleading purposes is not fair and may not be lawful.
What is not covered by the Data Protection Act
the right to be informed; all the other individual rights, except rights related to automated individual decision-making including profiling; the communication of personal data breaches to individuals; and. all the principles, but only so far as they relate to the right to be informed and the other individual rights.
What does the Data Protection Act only apply to
The Data Protection Act covers data held electronically and in hard copy, regardless of where data is held. It covers data held on and off campus, and on employees' or students' mobile devices, so long as it is held for University purposes, regardless of the ownership of the device on which it is stored.
What are the 3 parts of the golden rule
The Three C's that Make the Golden RuleCivility – What you say and how you say it does matter.Common good – It cannot be all about “you.”Curiosity – There are so many good ideas out there.
How many data protection rules are there
The GDPR sets out seven principles for the lawful processing of personal data. Processing includes the collection, organisation, structuring, storage, alteration, consultation, use, communication, combination, restriction, erasure or destruction of personal data.
What are the 5 pillars of data protection
The five pillars are integrity of data in its original form, availability for authorized parties, identity authenticity, data confidentiality and non-repudiation.
What is principle 7 of the Data Protection Act and how can it be avoided
7Appropriate technical and organisational measures shall be taken against unauthorised or unlawful processing of personal data and against accidental loss or destruction of, or damage to, personal data.
What is the 8 principle of Data Protection Act 1998
International Transfer of Data (Principle 8 of the DPA 1998)
“All provisions in this Chapter shall be applied in order to ensure that the level of protection of natural persons guaranteed by this Regulation is not undermined.”
What is the maximum fine for failing to comply with the 7 principles
What is the higher maximum The higher maximum amount, is £17.5 million or 4% of the total annual worldwide turnover in the preceding financial year, whichever is higher.
What is the maximum time you can hold data for
You can keep personal data indefinitely if you are holding it only for: archiving purposes in the public interest; scientific or historical research purposes; or. statistical purposes.
What is principle 4 of the Data Protection Act
The fourth data protection principle is that personal data undergoing processing must be accurate and, where necessary, kept up to date.
What is principle 5 of the Data Protection Act
5 GDPR Principles relating to processing of personal data. Personal data shall be: processed lawfully, fairly and in a transparent manner in relation to the data subject ('lawfulness, fairness and transparency');
What is principle 5 of the data protection Act
The fifth data protection principle is that personal data must be kept for no longer than is necessary for the purpose for which it is processed.
What is principle 4 of the data protection Act
Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: Any processing of personal data should be lawful and fair. It should be transparent to individuals that personal data concerning them are collected, used, consulted, or otherwise processed and to what extent the personal data are or will be processed.
What does data protection law only apply to
Depending on the situation, they could become victims of identity theft, discrimination or even physical harm. Generally speaking, data protection law applies to all workplaces, business ventures, societies, groups, clubs and enterprises of any type.
What does data protection not apply to
Article 2 of the GDPR states that the GDPR doesn't apply to a "purely personal or household activity."