protection more important than ever. It involves implementing measures to prevent unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction of data.
Summary of the Article in h2 with Key Points in 10 Paragraphs Each Paragraph for 3000 Characters:
1. The Data Protection Act 1998 and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) both include principles to ensure fair and lawful processing of personal data.
2. The principles of data protection apply to all aspects of processing personal data, including collection, storage, and communication.
3. The basic principles of data protection include lawfulness, fairness, and transparency. Individuals should be informed about the collection and use of their personal data.
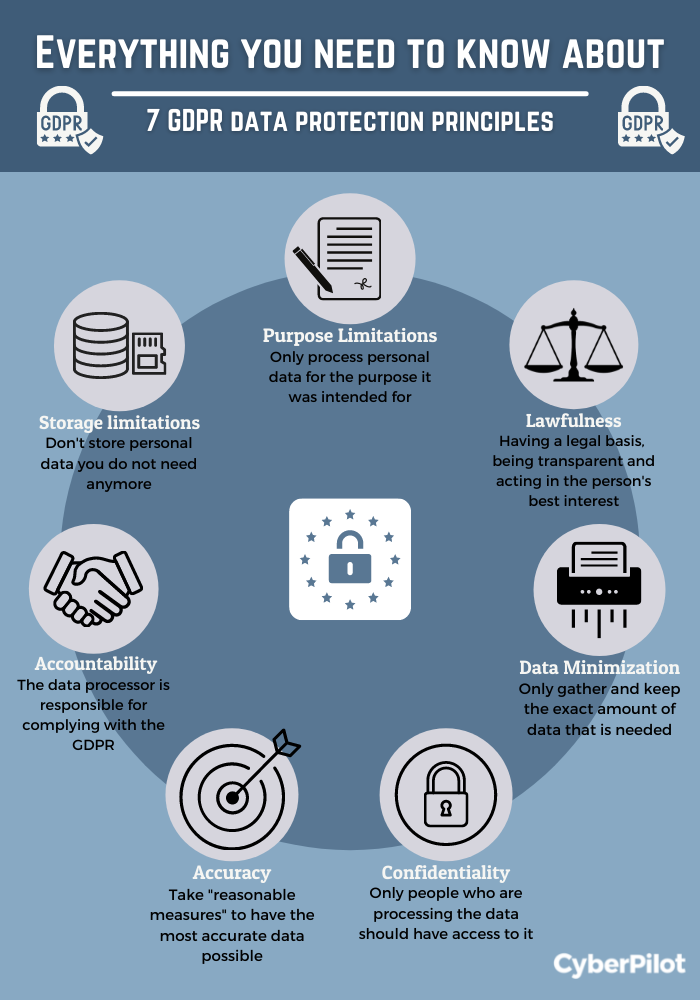
4. Purpose limitation means that personal data should only be processed for the specific purposes it was collected for.
5. Data minimization refers to the practice of limiting the collection of personal data to what is necessary for the intended purpose.
6. Accuracy of personal data is crucial, and organizations should make efforts to keep the data up to date and correct.
7. The storage limitation principle states that personal data should not be kept for longer than necessary.
8. Integrity and confidentiality are essential principles to protect personal data from unauthorized access or alteration.
9. The accountability principle requires organizations to demonstrate compliance with data protection principles and regulations.
10. The five pillars of data protection include integrity, availability, identity authenticity, data confidentiality, and non-repudiation.
11. The seventh principle of the Data Protection Act focuses on taking appropriate technical and organizational measures to prevent unauthorized processing or loss of personal data.
12. Data protection aims to safeguard sensitive information from damage, loss, or corruption, especially as the volume of data continues to grow exponentially.
15 Unique Questions Based on Text:
1. What are the eight data protection principles?
2. What do the seven principles of data protection apply to?
3. What are the basic principles of data protection?
4. What are the six essential data protection methods?
5. Are there 10 principles of data protection?
6. What are the five pillars of data protection?
7. What is principle 7 of the Data Protection Act and how can it be avoided?
8. What is data protection in simple words?
9. How does the law ensure fair and lawful processing of personal data?
10. How can organizations ensure transparency in data processing?
11. What are the consequences of not complying with data protection principles?
12. How can personal data accuracy be maintained?
13. What measures can be taken to protect personal data from unauthorized access?
14. How can organizations demonstrate compliance with data protection principles?
15. Why is data protection important in today’s digital age?
Detailed Answers:
1. The eight data protection principles include fairness and lawfulness, purposes, adequacy, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity and confidentiality, and accountability.
2. The seven principles of data protection apply to the processing of personal data in various activities, such as collection, storage, alteration, consultation, and communication.
3. The basic principles of data protection ensure that personal data processing is done lawfully, fairly, and transparently. Individuals should be informed about the collection and use of their data.
4. The six essential data protection methods are lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity and confidentiality.
5. Yes, there are ten principles of data protection, which include lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity and confidentiality, and accountability.
6. The five pillars of data protection are integrity of data in its original form, availability for authorized parties, identity authenticity, data confidentiality, and non-repudiation.
7. Principle 7 of the Data Protection Act addresses the need for appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data against unauthorized processing, accidental loss, or destruction.
8. Data protection in simple words refers to the process of safeguarding sensitive information from damage, loss, or corruption. It involves implementing measures to prevent unauthorized access or alteration of data.
9. The law ensures fair and lawful processing of personal data through the principles of data protection, which require organizations to collect and use personal data only for lawful and fair purposes.
10. Organizations can ensure transparency in data processing by informing individuals about the collection, use, and purpose of their personal data through privacy policies or consent forms.
11. The consequences of not complying with data protection principles can include fines, legal actions, damage to reputation, loss of customer trust, and potential data breaches.
12. Personal data accuracy can be maintained by regularly updating and verifying the data, ensuring proper data entry procedures, and providing individuals with the opportunity to correct their information.
13. Measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access can include using secure networks and encryption, implementing access controls and authentication processes, and regularly monitoring and auditing systems.
14. Organizations can demonstrate compliance with data protection principles by documenting their data processing activities, implementing privacy policies and procedures, conducting regular data protection impact assessments, and training employees on data protection practices.
15. Data protection is important in today’s digital age because the amount of data being created and stored has increased, making individuals and organizations more vulnerable to data breaches, identity theft, and misuse of personal information.
What are the 8 data protection principles
What are the Eight Principles of the Data Protection Act
| 1998 Act | GDPR |
|---|---|
| Principle 1 – fair and lawful | Principle (a) – lawfulness, fairness and transparency |
| Principle 2 – purposes | Principle (b) – purpose limitation |
| Principle 3 – adequacy | Principle (c) – data minimisation |
| Principle 4 – accuracy | Principle (d) – accuracy |
What do the seven principles of data protection apply to
The GDPR sets out seven principles for the lawful processing of personal data. Processing includes the collection, organisation, structuring, storage, alteration, consultation, use, communication, combination, restriction, erasure or destruction of personal data.
What are the basic principles of data protection
Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: Any processing of personal data should be lawful and fair. It should be transparent to individuals that personal data concerning them are collected, used, consulted, or otherwise processed and to what extent the personal data are or will be processed.
What are the six 6 essential data protection methods
We take a look at each principle in this blog, and provide advice on how they should fit within your GDPR compliance practices.Lawfulness, fairness and transparency.Purpose limitation.Data minimisation.Accuracy.Storage limitation.Integrity and confidentiality.
Are there 10 principles of data protection
FormatLawfulness, fairness and transparency.Purpose limitation.Data minimisation.Accuracy.Storage limitation.Integrity and confidentiality (security)Accountability principle.
What are the 5 pillars of data protection
The five pillars are integrity of data in its original form, availability for authorized parties, identity authenticity, data confidentiality and non-repudiation.
What is principle 7 of the data protection Act and how can it be avoided
7Appropriate technical and organisational measures shall be taken against unauthorised or unlawful processing of personal data and against accidental loss or destruction of, or damage to, personal data.
What is data protection in simple words
Data protection is the process of protecting sensitive information from damage, loss, or corruption. As the amount of data being created and stored has increased at an unprecedented rate, making data protection increasingly important.
How many key data protection principles are there
What are the principles Article 5 of the UK GDPR sets out seven key principles which lie at the heart of the general data protection regime.
What are the 4 pillars of data protection
Protect against these threats by implementing the four pillars of data protection; assessment, governance, training, and response.
Why is the 8 principles for data protection Act important
As a business service provider, we also deal with personal data given by customers. The 8 Principles of Data Protection Act 1998 make sure our personal information is safe. It is a vital step for businesses to secure their customer's personal data by following the laws.
What are the three A’s of security and data protection
The CIA triad refers to an information security model made up of the three main components: confidentiality, integrity and availability.
What are the 4 levels of data protection
Data Classification Levels
These can be adopted by commercial organizations, but, most often, we find four levels, Restricted, Confidential, Internal, Public.
What is principle 6 of data protection
What is the sixth principle about “Appropriate security” includes “protection against unauthorised or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction or damage”.
What is another name for data protection
Data protection is also known as data privacy or information privacy.
What are two ways to protect data
Here are some practical steps you and your staff can take to improve your data security.Back up your data.Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.Be aware of your surroundings.Be wary of suspicious emails.Install anti-virus and malware protection.Protect your device when it's unattended.
What are the 3 levels of data protection
Levels of Data ProtectionAuthentication.Authorization.Access Auditing and Analysis.
What are the three C’s of security
The 3Cs of Best Security: Comprehensive, Consolidated, and Collaborative – Check Point Blog.
What are the four 4 key issues in data security
Below are several common issues faced by organizations of all sizes as they attempt to secure sensitive data.Accidental Exposure.Phishing and Other Social Engineering Attacks.Insider Threats.Ransomware.Data Loss in the Cloud.SQL Injection.Data Discovery and Classification.Data Masking.
What is principle 4 of the Data Protection Act
The fourth data protection principle is that personal data undergoing processing must be accurate and, where necessary, kept up to date.
What are the three categories of data protection
Roughly speaking, data protection spans three broad categories, namely, traditional data protection (such as backup and restore copies), data security, and data privacy as shown in the Figure below.
What are three 3 security techniques that can be used to protect data
Enforcing communication via secure channels. Performing strong identity verification to ensure devices are not compromised. Limiting the use of third-party software and browsing to unsafe websites. Encrypting data on the device to protect against device compromise and theft.
What are the three types of data should be protected
There are three core elements to data security that all organizations should adhere to: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability.
What are the 3 A’s of data security
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) is a three-process framework used to manage user access, enforce user policies and privileges, and measure the consumption of network resources.
What are the three states of data
The three states of data are data at rest, data in motion and data in use. Data can change states quickly and frequently, or it may remain in a single state for the entire life cycle of a computer.