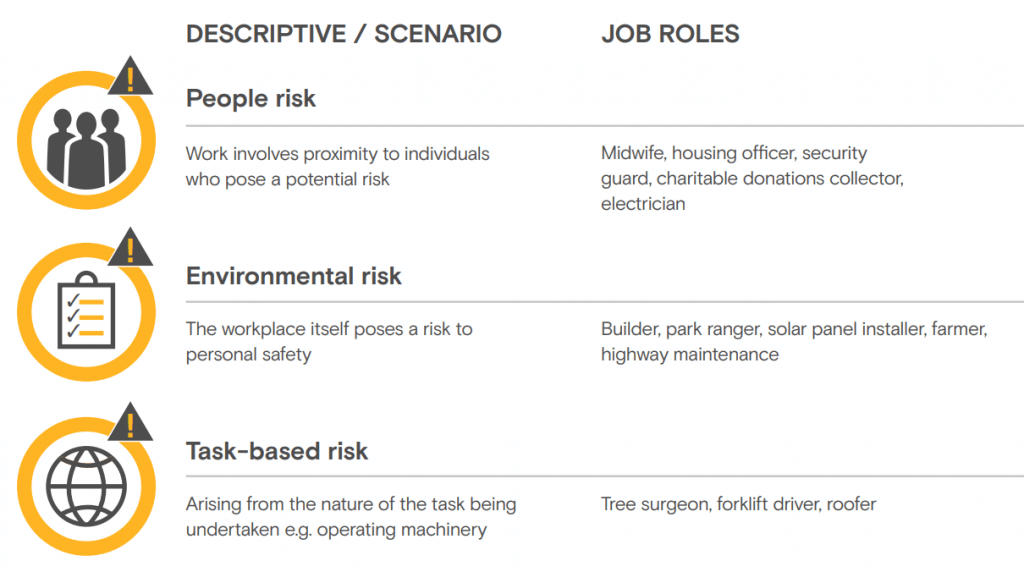
Risks that particularly affect lone workers include violence in the workplace, stress and mental health or wellbeing, and a person’s medical suitability to work alone. These factors can significantly impact the safety and security of individuals who work alone.
A dynamic risk assessment in lone working should consider three key elements, often referred to as the 3 A’s: the property, the people the lone worker is with, and the safeguards in place to protect themselves. Assessing these factors helps to ensure that the working environment is safe and secure.
Hazards associated with working alone include an increased risk of confrontations or violence, especially during late-night hours. It is crucial for lone workers to be able to receive assistance if they are injured or encounter an emergency situation. Adequate measures should be put in place to ensure the health and safety of lone workers.
A lone worker risk assessment is a process of identifying and assessing risks specifically associated with a job role performed by a lone worker. This assessment helps in determining potential risks and implementing appropriate measures to mitigate them.
Conducting a risk assessment at the workplace involves three key conditions. Firstly, identifying hazards that may cause injury or illness. Secondly, determining the likelihood and severity of harm that may arise from these hazards. Finally, taking action to eliminate or control the identified risks effectively.
Some common workplace hazards include slips, trips, falls, exposure to loud noises, working from heights, vibrations, and unguarded machinery. Different occupations have their unique challenges, which can pose physical risks to employees.
Risk assessment comprises three critical steps: risk identification, risk analysis, and risk evaluation. These stages help in identifying potential risks, analyzing their impacts, and evaluating the level of risk to determine appropriate control measures.
The three principles of risk assessment involve identifying hazards, evaluating the associated risks, and taking action to eliminate or control these risks. This systematic approach ensures that potential risks are adequately addressed to create a safer working environment.
Under the OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) guidelines, there is no specific requirement for a work alone policy. However, failure to have such a policy could be seen as a breach of the General Duty clause, which states that employers must provide a safe working environment.
Lone working risk assessments are a legal requirement and should be conducted for all employees. If a company employs five or more people, they are obligated to document and maintain a record of their risk assessments to ensure compliance with legal standards.
There are two main categories of risk assessment methodologies: quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative assessments involve assigning numerical values to risks, while qualitative assessments focus on subjective evaluations of risks based on expert judgment and experience.
The three elements of risk are the likelihood, consequences, and vulnerability. Assessing these factors helps in understanding the potential impact of risks and developing appropriate strategies to manage and mitigate them effectively.
What are 3 risks to lone worker
Risks that particularly affect lone workers include: violence in the workplace. stress and mental health or wellbeing. a person's medical suitability to work alone.
What are the 3 A’s you should consider when completing a dynamic risk assessment in lone working
A dynamic risk assessment may include a consideration of the property, whether it is safe to enter, whether the people they are with are potentially aggressive, and whether there are sufficient safeguards in place to protect themselves in the event of an incident.
What are the hazards associated with working alone
Lone workers may be at increased risk of confrontations or even violence, particularly if they are on shift during late night hours. Lone workers must be able to get assistance if they are injured or there is an emergency. See our resources for information on ensuring the health and safety of lone workers.
What is lone working risk assessment
What is a lone worker risk assessment A lone working risk assessment is a process of identifying and assessing risks associated with a job role carried out by a lone worker.
What are three 3 conditions required in conducting risk assessment at workplace
identify what could cause injury or illness in your business (hazards) decide how likely it is that someone could be harmed and how seriously (the risk) take action to eliminate the hazard, or if this isn't possible, control the risk.
What are 3 examples of common workplace hazards
Examples of physical hazards include slips, trips, falls, exposure to loud noises, working from heights, vibrations, and unguarded machinery. Every occupation places certain strains on a worker's body.
What are the 3 risk assessments
Risk assessment is the name for the three-part process that includes:Risk identification.Risk analysis.Risk evaluation.
What are the 3 principles of risk assessment
identify what could cause injury or illness in your business (hazards) decide how likely it is that someone could be harmed and how seriously (the risk) take action to eliminate the hazard, or if this isn't possible, control the risk.
What is the OSHA rule on working alone
Lone Working Legislation USA
OSHA does not have a specific requirement to develop and implement a work alone policy. But failure to have a policy could be considered a breach of General Duty OSHA requirements and has been cited by OSHA in the past under the General Duty statute.
Do I need a risk assessment for lone working
Are lone working risk assessments a legal requirement Lone working risk assessments are a basic legal requirement and should be carried out for all employees. If you employ five or more people, you are legally required to write down and keep a record of your risk assessment.
What are the two categories of risk assessment or
There are two main types of risk assessment methodologies: quantitative and qualitative.
What are the 3 elements of risk
The relative risk assessment chart uses three risk components:values.hazard.probability.
What are 3 of the 6 main categories of workplace hazards
Workplace hazards fall into six core types – safety, biological, physical, ergonomic, chemical and workload.1) Safety hazards.2) Biological hazards.3) Physical hazards.4) Ergonomic hazards.5) Chemical hazards.6) Workload hazards.
What are the categories of hazards
There are many types of hazards – chemical, ergonomic, physical, and psychosocial, to name a few – which can cause harm or adverse effects in the workplace. Get resources on specific hazards and their control, including identification, risk assessment and inspections, to keep your workplace healthy and safe.
What is a Level 3 risk assessment
Level 3 Award in Risk Assessment Overview
This regulated and nationally recognised qualification is specifically designed to provide learners with the knowledge and skills required to conduct risk assessments in low risk premises.
What is a Tier 3 risk assessment
A Tier 3 RA will involve the development of complex models supported by further intensive site investigations of the contaminants of concern, pathways, and receptors characteristics.
What are the 3 components of risk and explain each
From a project manager's perspective, there are three components of risk management: The actual risk, or event, itself. The likelihood that the event will occur. The final consequences of the event.
Are there rules around a single employee being alone in the office
People who work alone face the same hazards in their daily work as other workers. However, for lone workers the potential for harm is often greater. So it is essential that the risks of lone working are taken into account when risk assessments are carried out. There is no general legal prohibition on working alone.
What is the OSHA 2 man rule
Two-person rule.
Two people are required for work: In most situations where a worker is exposed to contact with lines or equipment energized at more than 600 volts. (See 1910.269(l)(1)(i).) Involving certain tasks performed by tree crews, including trimming trees or roping branches near energized lines.
Who conducts risk assessments for lone workers
As an employer, you must manage any health and safety risks before people can work alone. This applies to anyone contracted to work for you, including self-employed people. Lone workers are those who work by themselves without close or direct supervision, for example: as delivery drivers, health workers or engineers.
What are the 3 types of risk assessment
For the purpose of this article we will focus on three types of risk assessments:Baseline risk assessments (Baseline HIRA)Issue based risk assessments (Issue based HIRA)Continues risk assessments (Continues HIRA)
What are the 3 types of risk assessment we conduct
There are three types of risk assessments, baseline, issue-based and continuous risk assessments.
What are the 3 stages of risk assessment
Risk management has three (3) main stages, risk identification, risk assessment and risk control.
What are the 3 types of hazards that can be identified in the hazards identification section section 2 of the SDS
The CLP Regulation introduce several different classification hazards under the groups; physical, health and environmental. These hazards can range from acute toxicity to environmental hazards to skin sensitisation.
What are the categories of hazards for OSHA
Health hazards include chemical hazards (solvents, adhesives, paints, toxic dusts, etc.), physical hazards (noise, radiation, heat, etc.), biological hazards (infectious diseases), and ergonomic risk factors (heavy lifting, repetitive motions, vibration).