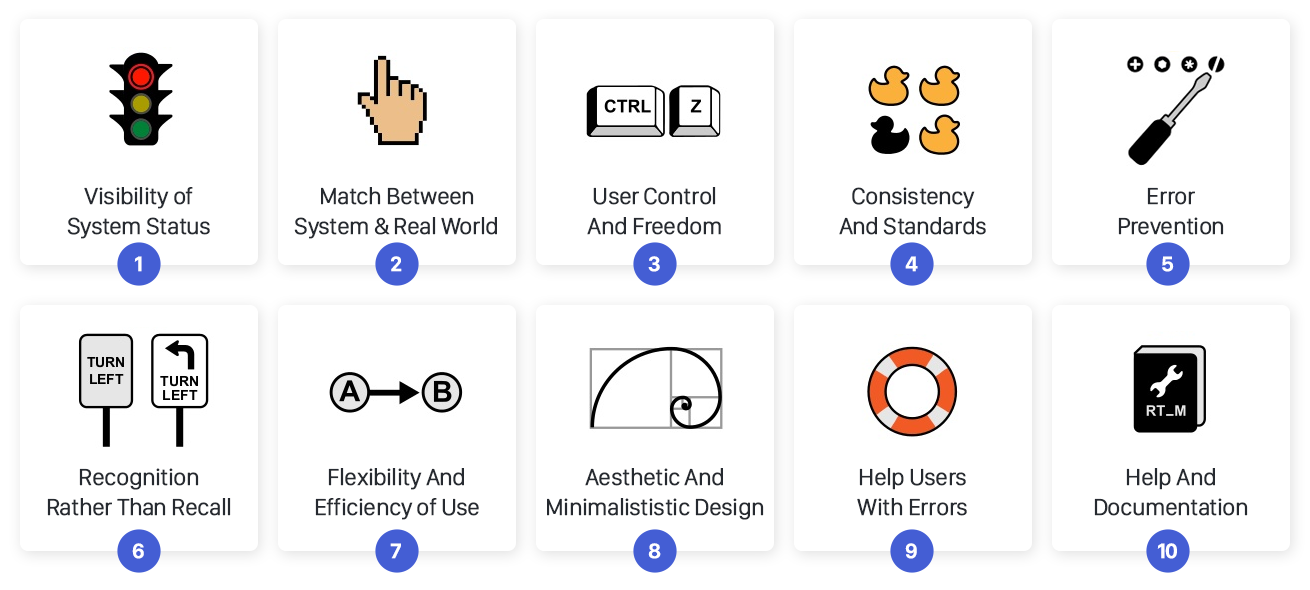
Nielsen’s 10 Usability Heuristics
1. Visibility of system status – The system should always keep users informed about its current state or status.
2. Match between system and the real world – The system should use language and concepts familiar to the users, making it easier for them to understand and interact with.
3. User control and freedom – Users should have the ability to easily undo actions or navigate away from a particular state or action without any hassle.
4. Consistency and standards – The system should follow established conventions and guidelines to maintain consistency throughout the user interface.
5. Error prevention – The system should be designed in a way that prevents errors from occurring in the first place, or provide clear and helpful error messages when they do occur.
6. Recognition rather than recall – The system should minimize the need for users to remember information by providing clear and visible cues and options.
7. Flexibility and efficiency of use – The system should cater to both novice and expert users, providing shortcuts and efficient ways of performing tasks.
8. Aesthetic and minimalist design – The system should have a clean and visually pleasing design that helps users focus on the content and tasks at hand.
9. Help users recognize, diagnose, and recover from errors – The system should provide clear and actionable error messages and guidance to help users recover from mistakes.
10. Help and documentation – The system should offer sufficient help and documentation to assist users in understanding and using the interface effectively.
15 Questions about Nielsen’s 10 Usability Heuristics:
1. What are Nielsen’s 10 usability heuristics?
The 10 Nielsen usability heuristics are: Visibility of system status, Match between system and the real world, User control and freedom, Consistency and standards, Error prevention, Recognition rather than recall, Flexibility and efficiency of use, Aesthetic and minimalist design, Help users recognize, diagnose, and recover from errors, Help and documentation.
2. Who created the 10 usability heuristics?
Jakob Nielsen created the 10 usability heuristics for user-interface design.
3. What is an example of Nielsen heuristic evaluation?
An example of a Nielsen heuristic evaluation is when a search engine like Google provides suggestions or corrects misspelled words as the user is typing, helping them avoid mistakes.
4. What is Jakob Nielsen’s heuristic evaluation?
Jakob Nielsen’s heuristic evaluation is a usability inspection method for assessing the compliance of a user interface design with recognized usability principles or heuristics.
5. How many types of heuristics are there?
There are four common types of heuristics: affect, anchoring, availability, and representativeness.
6. What are the principles of the heuristic method?
The principles of the heuristic method include: understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating and adapting as needed.
7. How do the Nielsen heuristics help in user-interface design?
The Nielsen heuristics provide a set of guidelines or rules of thumb that can help inform design decisions and improve the usability of user interfaces.
8. How can the visibility of system status be achieved in a user interface?
The visibility of system status can be achieved by providing clear and visible indicators, progress bars, or notifications that inform users about the current state or progress of a task or process.
9. What does it mean to have a match between the system and the real world in user interface design?
Having a match between the system and the real world means using language, concepts, and interaction patterns that are familiar to the users, making it easier for them to understand and use the system.
10. What does user control and freedom mean in user interface design?
User control and freedom refer to giving users the ability to easily undo actions, navigate through different states or screens, and recover from errors without any negative consequences.
11. Why is consistency and standards important in user interface design?
Consistency and standards help users develop mental models and expectations about how the interface will behave, making it easier for them to navigate and use the system.
12. How can error prevention be achieved in user interface design?
Error prevention can be achieved by incorporating validation checks, providing clear and specific error messages, and designing the interface in a way that minimizes the likelihood of errors occurring.
13. What is the difference between recognition and recall in user interface design?
Recognition refers to identifying something when it is presented to you, while recall requires you to retrieve information from memory. User interfaces should aim to rely more on recognition rather than recall to make tasks easier to perform.
14. How can flexibility and efficiency of use be incorporated into a user interface?
Flexibility and efficiency of use can be achieved by providing shortcuts, customizable settings, and options for advanced users, while still catering to the needs of novice users.
15. Why is help and documentation important in user interface design?
Help and documentation provide users with additional information, instructions, or support that can assist them in understanding and using the system effectively.
What is Nielsen’s 10 heuristics
Here are the 10 Nielsen heuristics:Visibility of system status;Match between system and the real world;User control and freedom;Consistency and standards;Error prevention;Recognition rather than recall;Flexibility and efficiency of use;Aesthetic and minimalist design;
Cached
What are the Nielsen’s heuristics
The Nielsen-Molich heuristics state that a system should: Keep users informed about its status appropriately and promptly. Show information in ways users understand from how the real world operates, and in the users' language. Offer users control and let them undo errors easily.
Cached
Which one is Jakob Nielsen’s 10 usability heuristics for UI design
Nielsen's 10 Usability HeuristicsVisibility of system status.Match between system and the real world.User control and freedom.Consistency and standards.Error prevention.Recognition rather than recall.Flexibility and efficiency of use.Aesthetic and minimalist design.
Cached
Who created the 10 usability heuristics
Jakob Nielsen’s
Jakob Nielsen's 10 usability heuristics for user-interface design have been widely used as broad rules of thumb for guiding design decisions since their original introduction in 1994.
What is an example for Nielsen heuristic evaluation
Example: When performing a search on Google, it helps them not to make mistakes in two moments, first, when they give us suggestions of words or expressions while typing, then, correcting the misspelled word.
What is Jacob Nielen’s heuristic evaluation
A heuristic evaluation is a usability inspection method for computer software that helps to identify usability problems in the user interface (UI) design. It specifically involves evaluators examining the interface and judging its compliance with recognized usability principles (the "heuristics").
How many types of heuristics are there
The four common types of heuristics include affect, anchoring, availability, and representativeness.
What are the principles of the heuristic method
Four principles
Try to understand the problem. Make a plan. Carry out this plan. Evaluate and adapt.
What are heuristics examples
When you see a person with their hood up in a dark alley and you decide to subtly walk past a bit faster, your brain has probably used a heuristic to evaluate the situation instead of a full thought-out deliberation process.
What are common examples of heuristics
Common sense heuristics is a practical and prudent approach that is applied to a decision where the right and wrong answers seem relatively clear cut.If it is raining outside, you should bring an umbrella.You choose not to drive after having one too many drinks.You decide not to eat food if you don't know what it is.
How do you conduct a heuristic evaluation by Jakob Nielsen
Jakob Nielsen's 10 Heuristic EvaluationVisibility of system status.Match between system and the real world.User control and freedom.Consistency and standards.Error prevention.Recognition rather than recall.Flexibility and efficiency of use.Aesthetic and minimalist design.
What are the most common heuristics
The four common types of heuristics include affect, anchoring, availability, and representativeness.
How many heuristic principles are there
10
Summary: Jakob Nielsen's 10 general principles for interaction design. They are called "heuristics" because they are broad rules of thumb and not specific usability guidelines.
What are the different types of heuristic methods
The four common types of heuristics include affect, anchoring, availability, and representativeness.
What are examples of heuristic approaches
Availability, anchoring, confirmation bias, and the hot hand fallacy are some examples of heuristics people use in their economic lives.
What are examples of take the best heuristic
Example 1 – Elections
As a result, we tend to use the take-the-best heuristic to decide which candidate to vote for. We vote for the candidate we think will best address one major issue, instead of informing ourselves on their stance for multiple issues.
What is a real life example of affect heuristic
For example, you can probably sense the different feelings associated with the word “love” as opposed to the word “hate.” When we subconsciously let these feelings guide our decisions, we rely on the affect heuristic. This is because we perceive reality in two fundamentally different ways or systems.
What are the steps in heuristic evaluation
Here are the steps to ensure that your heuristic evaluation yields maximum results:Step 1: Define the scope of your evaluation.Step 2: Know your end-user.Step 3: Choose your set of heuristics.Step 4: Set up an evaluation system and identify issues.Step 5: Analyze and summarize findings.
What is a real life example of heuristics
When you see a person with their hood up in a dark alley and you decide to subtly walk past a bit faster, your brain has probably used a heuristic to evaluate the situation instead of a full thought-out deliberation process.
What is the most common heuristic
The most common examples of heuristics are the availability, representativeness, and affect heuristics. However, there are many more possible examples, as shown in the 23 listed below.
What are the 4 types of heuristics
Each type of heuristic is used for the purpose of reducing the mental effort needed to make a decision, but they occur in different contexts.Availability heuristic.Representativeness heuristic.Anchoring and adjustment heuristic.Quick and easy.
What is a real life example of heuristics in psychology
When you see a person with their hood up in a dark alley and you decide to subtly walk past a bit faster, your brain has probably used a heuristic to evaluate the situation instead of a full thought-out deliberation process.
What is a good example of heuristic
When you see a person with their hood up in a dark alley and you decide to subtly walk past a bit faster, your brain has probably used a heuristic to evaluate the situation instead of a full thought-out deliberation process.
What are the heuristic techniques
The most common heuristic methods are – trial and error, guesswork, the process of elimination, historical data analysis. These methods involve simply available information that is not particular to the problem but is most appropriate. They can include representative, affect, and availability heuristics.
What are the 6 stages of heuristic inquiry
This article describes the six phases of the heuristic method: initial engagement, immersion, incubation, illumination, explication, and creative synthesis.