Summary of the Article:
The human rights of the internet include:
- The right to privacy online, which includes freedom from surveillance, the use of encryption, and online anonymity.
- The right to data protection, including control over personal data collection, retention, processing, disposal, and disclosure.
- The protection against arbitrary or unlawful interferences with privacy, family, home, or correspondence.
- The right to access, use, create, and publish digital media, as well as access and use computers, electronic devices, and communication networks.
- The freedom to access and use the internet without discriminatory taxes.
- The decentralized nature of the internet, with no single entity having ownership or control over it.
- The violation of human privacy occurs when states interfere with or penalize actions that only concern the individual, such as not wearing safety equipment at work or committing suicide.
Key Points:
1. Everyone has the right to privacy online, including freedom from surveillance and the use of encryption and online anonymity.
2. Everyone has the right to protect their personal data, including control over its collection, retention, processing, disposal, and disclosure.
3. The right to privacy in the digital age is safeguarded as a human right under Article 17 of the ICCPR.
4. California’s Online Privacy Protection Act requires operators to post a privacy policy on their websites or online services if they collect personally identifiable information from California residents for commercial purposes.
5. Digital rights are an extension of human rights for the internet age, allowing people to access, use, create, and publish digital media.
6. The law prohibits governments from taxing internet access and imposing discriminatory internet-only taxes.
7. The internet is a globally distributed network without a central governing body, with each network setting and enforcing its own policies.
8. Violations of human privacy occur when states interfere with actions that only concern the individual’s autonomy, such as not wearing safety equipment or committing suicide.
Questions and Answers:
1. What are the human rights of the internet?
The human rights of the internet include the right to privacy online, data protection, and access to digital media.
2. Is internet privacy a human right?
Yes, internet privacy is considered a human right and is protected under Article 17 of the ICCPR.
3. What laws protect online privacy?
California’s Online Privacy Protection Act requires operators to have a privacy policy if they collect personally identifiable information from California residents for commercial purposes.
4. What are the digital rights of users?
Digital rights encompass the rights to access, use, create, and publish digital media, as well as access and use computers and electronic devices. They are an extension of human rights for the internet age.
5. What are the Internet Freedom Acts?
The Internet Freedom Acts prohibit governments from taxing internet access and imposing discriminatory internet-only taxes.
6. Who owns the rights to the internet?
No single person, company, organization, or government owns the internet. It is a decentralized network with each constituent network having its own policies.
7. What constitutes a violation of human privacy?
A violation of human privacy occurs when states interfere with actions that solely concern the individual’s autonomy, such as not wearing safety equipment or committing suicide.
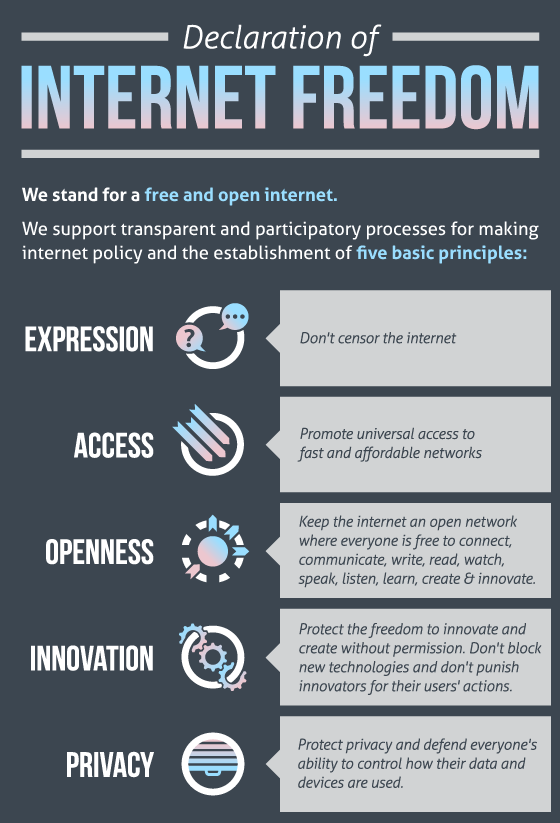
What are the human rights of the Internet
Everyone has the right to privacy online. This includes freedom from surveillance, the right to use encryption, and the right to online anonymity. Everyone also has the right to data protection, including control over personal data collection, retention, processing, disposal and disclosure.
Cached
Is internet privacy a human right
More specifically, Article 17 of the ICCPR protects everyone from arbitrary or unlawful interferences with their “privacy, family, home, or correspondence.” Through its international advocacy work, the ACLU is working to ensure that the right to privacy in the digital age is safeguarded as a human right.
What laws protect online privacy
California's Online Privacy Protection Act requires an operator, defined as a person or entity that collects personally identifiable information from California residents through an Internet Web site or online service for commercial purposes, to post a conspicuous privacy policy on its Web site or online service (which …
Cached
What are the digital rights of users
Digital rights, closely linked to freedom of expression and privacy, are those that allow people to access, use, create and publish digital media, as well as access and use computers, other electronic devices and communications networks. Digital rights are an extension of human rights for the Internet age.
What are the Internet freedom Acts
The law bars federal, state and local governments from taxing Internet access and from imposing discriminatory Internet-only taxes such as bit taxes, bandwidth taxes, and email taxes. It also bars multiple taxes on electronic commerce.
Who owns the rights to the Internet
No one person, company, organization or government runs the Internet. It is a globally distributed network comprising many voluntarily interconnected autonomous networks. It operates without a central governing body with each constituent network setting and enforcing its own policies.
What is violation of human privacy
The right to privacy is the right to individual autonomy that is violated when states interfere with, penalise, or prohibit actions that essentially only concern the individual, such as not wearing safety equipment at work or committing suicide.
What is the violation of the right to privacy
The Privacy Act allows for criminal penalties in limited circumstances. An agency official who improperly discloses records with individually identifiable information or who maintains records without proper notice, is guilty of a misdemeanor and subject to a fine of up to $5,000, if the official acts willfully.
What is an example of invasion of privacy on the Internet
For example, if you tape a private customer conversation without approval and use the remarks on your website, you could face an invasion of privacy lawsuit. Portraying someone in a false light. This occurs if something you say or publish puts a person in a negative light.
Is invasion of online privacy illegal
Yes, invasion of privacy is a crime and is punishable by the legal system.
What are the different types of user access rights
Types of access controlMandatory access control (MAC). This is a security model in which access rights are regulated by a central authority based on multiple levels of security.Discretionary access control (DAC).Role-based access control (RBAC).Rule-based access control.Attribute-based access control.
What is an example of user access rights
The type of access—for example, a user might be allowed to read data without modifying it (read only) or be allowed to read and write data. Specific functions a user can access—for example, most systems have an administrator role that allows users to change configuration or assign permissions to other users.
Are there laws on the Internet
Internet laws often incorporate and apply principles from different legal fields – such as privacy laws or contract laws – which pre-date the internet and can be open to interpretation. There is no single law regulating online privacy.
Is Internet protected by 1st Amendment
The First Amendment's protections apply to online speech as much as to offline speech. The First Amendment provides that “Congress shall make no law . . . prohibiting the freedom of speech.” This core principle applies whether the speech in question is shared in a public square or on the internet.
Who has control over the Internet
While the Internet is theoretically decentralized and thus controlled by no single entity, many argue that tech companies such as Amazon, Facebook, and Google represent a small concentration of organizations that have unprecedented influence over the information and money on the Internet.
Does the government control the Internet
Federal laws. With a few exceptions, the free speech provisions of the First Amendment bar federal, state, and local governments from directly censoring the Internet. The primary exception has to do with obscenity, including child pornography, which does not enjoy First Amendment protection.
What is the 14th Amendment right to privacy
In the Fourteenth Amendment, the right to privacy is implied by the guarantee of due process for all individuals, meaning that the state cannot exert undue control over citizens' private lives.
What is protected under the Privacy Act
The Privacy Act of 1974, as amended to present, including Statutory Notes (5 U.S.C. 552a), Protects records about individuals retrieved by personal identifiers such as a name, social security number, or other identifying number or symbol.
What counts as invasion of privacy
Invasion of privacy involves the infringement upon an individual's protected right to privacy through a variety of intrusive or unwanted actions. Such invasions of privacy can range from physical encroachments onto private property to the wrongful disclosure of confidential information or images.
What are the three 3 major Internet privacy issues
But the “top 3” privacy issues with most data breaches are “tracking, hacking and trading.” Let's take a closer look at each one and see how it impacts your privacy.
What is illegal to view on the Internet
Examples of illegal internet searches may include:
Child pornography. Criminals for hire. Joining online terrorist organizations. How to make homemade explosives. How to commit/clean up after a murder.
What is the right to privacy being violated
Invasion of privacy is a tort based in common law allowing an aggrieved party to bring a lawsuit against an individual who unlawfully intrudes into his/her private affairs, discloses his/her private information, publicizes him/her in a false light, or appropriates his/her name for personal gain.
What are the six types of permissions
There are six standard permission types which apply to files and folders in Windows:Full Control.Modify.Read & Execute.List Folder Contents.Read.Write.
What are the 3 types of access control
Types of access control systemsDiscretionary access control (DAC) A discretionary access control system, on the other hand, puts a little more control back into leadership's hands.Rule-based access control.Identity-based access control.
What are the 3 different types of access rights
Three main types of access control systems are: Discretionary Access Control (DAC), Role Based Access Control (RBAC), and Mandatory Access Control (MAC). DAC is a type of access control system that assigns access rights based on rules specified by users.
