Summary of the Article:
1. The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) was abolished on November 9, 1965, by the Department of Housing and Urban Development Act.
2. The FHA lasted from the 1930s through the late 1990s, providing government guarantees for long-term, low-risk loans.
3. One downfall of an FHA loan is the extra cost of an upfront mortgage insurance premium (MIP) of 2.25% of the loan’s value.
4. The FHA was successful in making important changes to how people could buy a home during the Great Depression.
5. Sellers may avoid FHA buyers due to concerns about FHA loan approval compared to conventional borrowers.
6. The Fair Housing Act has the potential to be powerful, but its effectiveness has been hindered by discrimination and ineffective enforcement.
7. FHA loans started in 1934 and have since served millions of homeowners and financed various housing projects.
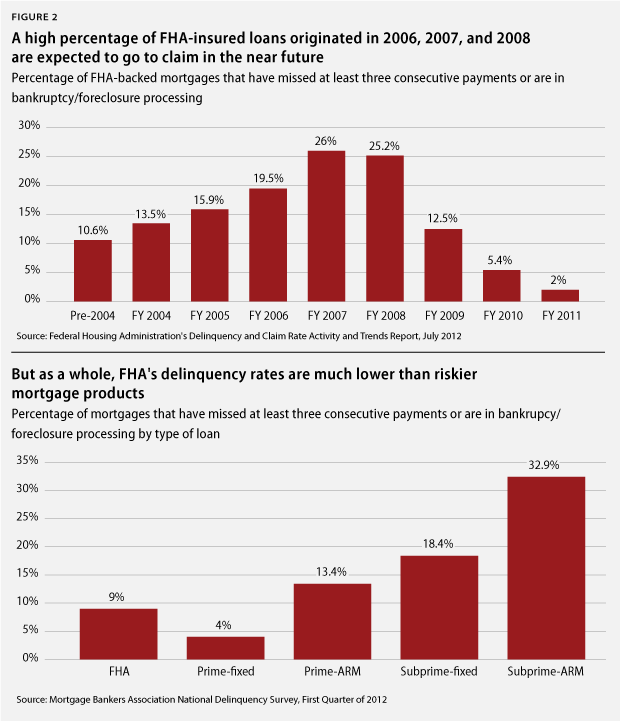
8. The last housing recession lasted from 2005 to 2007, resulting in a crash in home values.
Questions and Answers:
1. When was the FHA abolished?
Abolished: Effective November 9, 1965, by Department of Housing and Urban Development Act (79 Stat. 667), September 9, 1965. Successor Agencies: Department of Housing and Urban Development.
2. How long did the Federal Housing Administration last?
Since Congress created the Federal Housing Administration in the 1930s through the late 1990s, a government guarantee for long-term, low-risk loans—such as the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage—helped ensure that mortgage credit was continuously available for just about any creditworthy borrower.
3. What is the downfall of an FHA loan?
Here are some FHA home loan disadvantages: An extra cost – an upfront mortgage insurance premium (MIP) of 2.25% of the loan’s value. The MIP must either be paid in cash when you get the loan or rolled into the life of the loan. Home price qualifying maximums are set by FHA.
4. Was the FHA successful or not?
Yes, in 1934, in the middle of the Great Depression, the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) made some important changes to how people could buy a home that led to the modern mortgage system.
5. Why do sellers avoid FHA?
FHA loans help low-to-moderate-income borrowers with less-than-stellar credit become homeowners. Sellers may feel that FHA buyers are less likely to be approved for a loan than conventional borrowers.
6. Why did the Fair Housing Act fail?
The Fair Housing Act has the potential to be one of the most powerful laws in the country, but its effectiveness has been stymied by entrenched policies, practices, discrimination, segregation, and ineffective enforcement by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) and Department of…
7. When did FHA loans start?
1934. Since then, FHA has served nearly 44 million homeowners and financed various housing projects.
8. How long did the last housing recession last?
The last time the U.S. housing market looked frothy was back in 2005 to 2007. Then, home values crashed, with disastrous consequences. (Answer continued in the next question)
…s.
9. What were the consequences of the housing recession?
The consequences of the housing recession were the crashing of home values, widespread foreclosures, and a significant impact on the overall economy.
10. How did the FHA assist during the Great Depression?
The FHA made important changes to how people could buy a home during the Great Depression, ensuring mortgage credit was continuously available for creditworthy borrowers and leading to the modern mortgage system.
11. Are FHA loans still available today?
Yes, FHA loans are still available today and continue to provide assistance to low-to-moderate-income borrowers.
12. Can a borrower roll the upfront MIP into an FHA loan?
Yes, the upfront mortgage insurance premium (MIP) of 2.25% can be rolled into the life of the loan, providing borrowers with the option to finance the cost.
13. How has the FHA evolved over the years?
The FHA has continuously evolved over the years to adapt to changing housing market conditions and borrower needs, introducing various programs and initiatives to support affordable housing options.
14. What is the current role of the Department of Housing and Urban Development?
The Department of Housing and Urban Development plays a crucial role in developing and implementing housing policies, overseeing fair housing practices, and addressing various housing-related issues.
15. How can the Fair Housing Act be more effectively enforced?
The Fair Housing Act can be more effectively enforced through stricter regulations, increased funding for enforcement agencies, and raising awareness about fair housing rights and responsibilities among both the public and housing providers.
When was the FHA abolished
Abolished: Effective November 9, 1965, by Department of Housing and Urban Development Act (79 Stat. 667), September 9, 1965. Successor Agencies: Department of Housing and Urban Development.
How long did the Federal Housing Administration last
Since Congress created the Federal Housing Administration in the 1930s through the late 1990s, a government guarantee for long-term, low-risk loans—such as the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage—helped ensure that mortgage credit was continuously available for just about any creditworthy borrower.
Cached
What is the downfall of an FHA loan
Here are some FHA home loan disadvantages: An extra cost – an upfront mortgage insurance premium (MIP) of 2.25% of the loan's value. The MIP must either be paid in cash when you get the loan or rolled into the life of the loan. Home price qualifying maximums are set by FHA.
Was the FHA successful or not
Was the FHA successful Yes. In 1934, in the middle of the Great Depression, the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) made some important changes to how people could buy a home that led to the modern mortgage system.
Why do sellers avoid FHA
FHA Underwriting Worries Some Sellers
Because FHA loans help low- to moderate-income borrowers with less-than-stellar credit become homeowners, sellers may feel that FHA buyers are less likely to be approved for a loan than conventional borrowers.
Why did the Fair Housing Act fail
The Fair Housing Act has the potential to be one of the most powerful laws in the country, but its effectiveness has been stymied by entrenched policies and practices that perpetuate discrimination and segregation; ineffective enforcement by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) and Department of …
When did FHA loans start
1934
Since 1934, FHA has served nearly 44 million homeowners and financed more than 50,000 multifamily mortgages representing 4.8 million modestly priced rental housing units. FHA also finances residential care facilities, hospitals, manufactured housing, home improvements, and reverse mortgages.
How long did the last housing recession last
The last time the U.S. housing market looked so frothy was back in 2005 to 2007. Then home values crashed, with disastrous consequences.
Why do people not accept FHA loans
Some home sellers see the FHA loan as a riskier loan than a conventional loan because of its stricter approval and appraisal requirements. Additionally, the loan's more lenient financial requirements for borrowers may leave the seller with a negative perception.
What was the lasting impact of the FHA
Impact of the National Housing Act
The FHA was successful at stabilizing and then stimulating national housing markets and extending housing credit to Americans for whom homeownership had once been out of reach. FHA loans—mortgages insured by the FHA and issued by an FHA-approved lender—still exist today.
Why are FHA closing costs so high
Because FHA closing costs include the upfront MIP, an FHA loan can have average closing costs on the higher end of the typical 3% – 6% range. That doesn't diminish in any way the value of getting an FHA mortgage, with its low down payment, lower interest rates and flexible underwriting.
Why do realtors prefer conventional over FHA
Sellers often prefer conventional buyers because of their own financial views. Because a conventional loan typically requires higher credit and more money down, sellers often deem these reasons as a lower risk to default and traits of a trustworthy buyer.
What did the Fair Housing Act of 1968 end
The 1968 Act expanded on previous acts and prohibited discrimination concerning the sale, rental, and financing of housing based on race, religion, national origin, sex, (and as amended) handicap and family status. Title VIII of the Act is also known as the Fair Housing Act (of 1968).
How did the Housing Act of 1949 fail
While envisioned to address the national housing shortage by transitioning families from so-called “slums and firetraps” into safer public housing, the Act failed to recognize the cost of destroying the well-established communities in which these families lived.
Why doesn’t everyone use an FHA loan
FHA Underwriting Worries Some Sellers
Because FHA loans help low- to moderate-income borrowers with less-than-stellar credit become homeowners, sellers may feel that FHA buyers are less likely to be approved for a loan than conventional borrowers.
What was the original purpose of the FHA
History of the FHA
Its primary purpose was to improve housing standards and conditions, provide a method of mutual mortgage insurance, and reduce foreclosures on family home mortgages. The legislation created the Federal Savings and Loan Insurance Corp.
Will the housing bubble burst in 2023
Demand for homes remains high, and there are fewer home sellers than there were in 2022. And while the market is cooling, experts don't expect an actual housing crash or a housing bubble burst in 2023. Will there be a housing market crash in 2023 It's highly unlikely that the housing market will crash in 2023.
How much did housing drop in 2008 recession
However, when the subprime mortgage crisis hit and defaults began to soar, the bubble burst and housing prices fell dramatically. According to the S&P CoreLogic Case-Shiller U.S. National Home Price NSA Index, housing prices fell by 27.4% from their peak in 2006 to their low point in 2012.
Why are FHA loans less attractive to sellers
Of the respondents to the NAR survey we mentioned earlier, 35% cited low down payment, and 21% cited the small amount of earnest funds as an aspect of FHA loans that makes them less attractive to home sellers.
Do sellers prefer FHA or conventional
Sellers often prefer conventional buyers because of their own financial views. Because a conventional loan typically requires higher credit and more money down, sellers often deem these reasons as a lower risk to default and traits of a trustworthy buyer.
Was the FHA in 1934 successful
The National Housing Act and the FHA were wildly successful in supporting the great postwar boom in housing and suburbanization, in which the national home ownership rate jumped from under 50% to almost 70% of households.
What is an FHA loan and why are they so popular now
An FHA loan is a government-backed mortgage insured by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA). FHA home loans require lower minimum credit scores and down payments than many conventional loans, which makes them especially popular with first-time homebuyers.
Why are FHA loans unattractive to sellers
Not attractive to sellers – FHA loans are not attractive to sellers due to the strict inspection standards and requirements. This means the seller musts repair the items required by the FHA to close the loan. In some instances, FHA loans can take a little longer to close which is another negative for the sellers.
Should I switch from FHA to conventional
It's worth it to refinance an FHA loan to a conventional loan if you've built enough equity in your home and can get rid of costly monthly mortgage insurance. However, you'll need to determine if you can meet more stringent qualifying requirements before you trade your FHA loan for a conventional mortgage.
Why did Fair Housing Act fail
The Fair Housing Act has the potential to be one of the most powerful laws in the country, but its effectiveness has been stymied by entrenched policies and practices that perpetuate discrimination and segregation; ineffective enforcement by the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) and Department of …