Summary of the Article: What does an ultrasonic sensor do and how does it work?
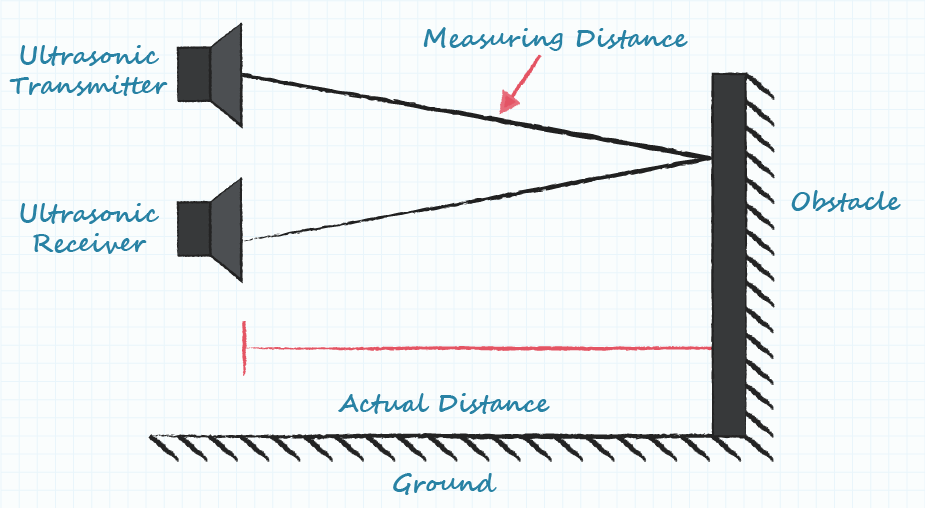
An ultrasonic sensor works by emitting sound waves at a frequency too high for humans to hear. It then waits for the sound to be reflected back and calculates the distance based on the time required. This is similar to how radar measures the time it takes a radio wave to return after hitting an object.
Key Points:
1. Ultrasonic sensor vs. motion sensor: The biggest difference between an IR sensor and an ultrasonic sensor is the way in which they work. Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves to determine the distance from an object, while IR sensors use infrared light to detect the presence of an object.
2. How does an ultrasonic sensor detect distance? Ultrasonic sensors measure the distance to a target object by sending a sound pulse above the range of human hearing (ultrasonic) towards the target. It then measures the time it takes for the sound echo to return.
3. Triggering an ultrasonic sensor: An ultrasonic sensor emits a sound pulse in the ultrasonic range, which propagates through the air until it encounters an object. The sound pulse then bounces off the object and is returned to the sensor as an “echo”.
4. Disadvantages of using ultrasonic sensors: Some common disadvantages of conventional ultrasonic sensors include limited testing distance, inaccurate readings, and inflexible scanning methods. However, these drawbacks can be mitigated with the right nondestructive testing (NDT) tools and techniques.
5. Range of an ultrasonic sensor: Ultrasonic transducers operate at frequencies ranging from 30-500 kHz for air-coupled applications. Low-frequency sensors (30-80 kHz) are more effective for long-range measurements, while high-frequency sensors are more effective for short-range measurements.
6. What can an ultrasonic sensor not detect? Ultrasonic sensors can detect objects regardless of their color, surface, or material, except for very soft materials like wool that absorb sound. They are also a reliable choice for detecting transparent or difficult-to-detect items where optical technologies may fail.
Questions:
1. What does an ultrasonic sensor do and how does it work?
An ultrasonic sensor emits sound waves at a frequency too high for humans to hear and calculates distance based on the time it takes for the sound to be reflected back.
2. What is the difference between a motion sensor and an ultrasonic sensor?
Motion sensors detect motion using various technologies, while ultrasonic sensors use sound waves to measure distance.
3. How does an ultrasonic sensor detect distance?
Ultrasonic sensors measure distance by sending out sound pulses and measuring the time it takes for the echo to return.
4. What triggers an ultrasonic sensor?
An ultrasonic sensor emits a sound pulse, which bounces off an object and returns as an echo to the sensor.
5. What are the disadvantages of using ultrasonic sensors?
Some disadvantages include limited testing distance, inaccurate readings, and inflexible scanning methods.
6. What is the range of an ultrasonic sensor?
The range depends on the frequency of the ultrasonic sensor, with low-frequency sensors being more effective for long-range measurements.
7. What can an ultrasonic sensor not detect?
Ultrasonic sensors cannot detect very soft materials like wool that absorb sound. They are also a reliable choice for detecting transparent or difficult-to-detect items.
8. How can the drawbacks of using ultrasonic sensors be overcome?
The drawbacks can be mitigated by using the right nondestructive testing tools and techniques.
9. Can ultrasonic sensors be used for presence detection?
Yes, ultrasonic sensors can detect the presence of objects regardless of color, surface, or material.
10. Are ultrasonic sensors effective for long-range measurements?
Yes, low-frequency ultrasonic sensors are more effective for long-range measurements.
11. Do ultrasonic sensors work well with transparent objects?
Yes, ultrasonic sensors are a reliable choice for detecting transparent objects where optical technologies may fail.
12. How do ultrasonic sensors compare to infrared sensors?
Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves, while infrared sensors use infrared light to detect objects.
13. What are some potential applications for ultrasonic sensors?
Ultrasonic sensors can be used for distance measurement, object detection, level sensing, proximity sensing, and more.
14. What factors should be considered when choosing an ultrasonic sensor?
Factors to consider include frequency range, measuring range, accuracy, power requirements, and environmental conditions.
15. How can ultrasonic sensors be used in robotics?
Ultrasonic sensors can be used to detect obstacles, measure distances, and assist in navigation for robotic systems.
What does an ultrasonic sensor do and how does it work
Ultrasonic sensors work by emitting sound waves at a frequency too high for humans to hear. They then wait for the sound to be reflected back, calculating distance based on the time required. This is similar to how radar measures the time it takes a radio wave to return after hitting an object.
Cached
What is the difference between motion sensor and ultrasonic sensor
The biggest difference between IR sensor vs. ultrasonic sensors is the way in which the sensor works. Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves (echolocation) to measure how far away you are from an object. On the other hand, IR sensors use Infrared light to determine whether or not an object is present.
Cached
How does ultrasonic sensor detect distance
Ultrasonic sensors (sometimes called ultrasonic transducers), measure the distance to or the presence of a target object by sending a sound pulse, above the range of human hearing (ultrasonic), toward the target and then measuring the time it takes the sound echo to return.
What triggers ultrasonic sensor
An ultrasonic sensor emits a sound pulse in the ultrasonic range. This sound pulse propagates at the speed of sound through air (about 344 meters per second) until the sound pulse encounters an object. The sound pulse bounces off the object and is returned in reverse to the sensor where this "echo" is received.
What are 3 disadvantages of using ultrasonic sensors
Some common disadvantages of conventional ultrasonic sensors include limited testing distance, inaccurate readings, and inflexible scanning methods. All of these drawbacks, however, can be mitigated and even overcome with the right NDT tools and techniques.
What is the range of an ultrasonic sensor
Ultrasonic transducers operate at frequencies in the range of 30–500 kHz for air-coupled applications. As the ultrasonic frequency increases, the rate of attenuation increases. Thus, low-frequency sensors (30–80 kHz) are more effective for long range, while high-frequency sensors are more effective for short range.
What can ultrasonic sensor not detect
For presence detection, ultrasonic sensors detect objects regardless of the color, surface, or material (unless the material is very soft like wool, as it would absorb sound.) To detect transparent and other items where optical technologies may fail, ultrasonic sensors are a reliable choice.
How far can ultrasonic sensors reach
This economical sensor provides 2cm to 400cm of non-contact measurement functionality with a ranging accuracy that can reach up to 3mm.
What interferes with ultrasonic sensors
If there are other sources of ultrasonic noise in the vicinity, the sensor will hear that and give an improper distance measurement. It is also possible for a previous pulse to echoed off multiple things and seem to trigger the sensor early.
How accurate is ultrasonic sensor distance
For example, an ultrasonic water level sensor reading a full-scale range of 12 feet or 144 inches will have an accuracy of ±0.144 inches (at ambient temperature and controlled conditions). The same sensor reading a distance of 75 inches will have an accuracy of ±0.075 inches.
How long can ultrasonic sensor detect
Long range detection: In industrial sensing, more and more applications require detection over distance. Ultrasonic sensors detect over long ranges up to forty feet, while limit switches and inductive sensors do not.
What can interfere with ultrasonic sensor
The relative humidity and temperature of the ambient atmosphere can affect the detection range of the ultrasonic signal. The detection range of an ultrasonic sensor can decrease as the temperature rises and as the humidity increases.
What are the disadvantages of ultrasonic sensors
Some common disadvantages of conventional ultrasonic sensors include limited testing distance, inaccurate readings, and inflexible scanning methods.
Can ultrasonic sensors go through walls
Ultrasonic waves behave more like light than sound. For example, music from your stereo can fill your entire house. Ultrasound cannot penetrate solid surfaces (walls, floors, ceilings) or travel around corners.
What happens if there is an object infront of the ultrasonic sensor
It sends an ultrasonic pulse out at 40kHz which travels through the air and if there is an obstacle or object, it will bounce back to the sensor.
What is the disadvantage of ultrasonic
Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Testing Techniques:
More expensive than other methods. Difficult to use on thin materials. Part Geometry can cause complications. Needs relatively smooth surface to couple transducer.
How reliable is ultrasonic sensor
For example, an ultrasonic water level sensor reading a full-scale range of 12 feet or 144 inches will have an accuracy of ±0.144 inches (at ambient temperature and controlled conditions). The same sensor reading a distance of 75 inches will have an accuracy of ±0.075 inches.
What is the lifespan of ultrasonic sensor
The MTBF of the MaxSonar product line is 232,896 hours, with a 90% confidence, for products operated at 45°C or less. Because no failures were observed during our testing, we believe that the values in this report can be taken as a conservative estimate of product lifetime.
What can block ultrasonic waves
Both glass and plastic, regardless of whether they are clear or not, are solid objects that impede sound. And our 42kHz ultrasonic sound wave cannot pass through them to complete a ranging cycle to the target beyond this shield.
Can ultrasonic go through walls
Ultrasonic waves behave more like light than sound. For example, music from your stereo can fill your entire house. Ultrasound cannot penetrate solid surfaces (walls, floors, ceilings) or travel around corners.