Summary of the Article:
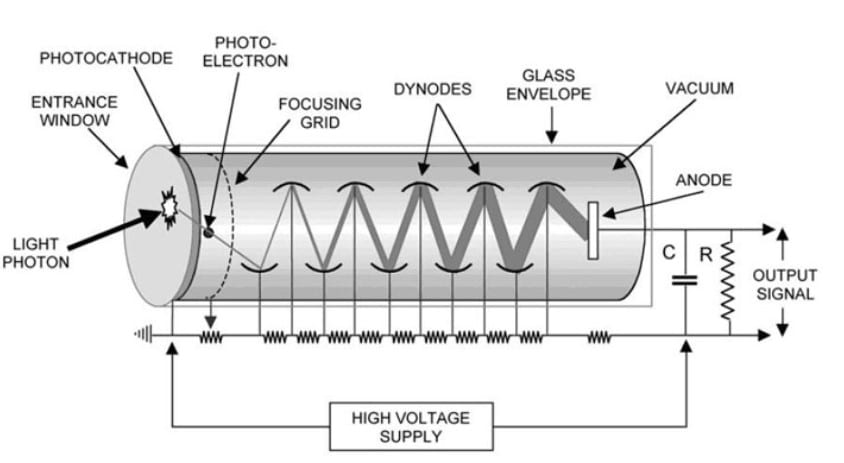
1. The working principle of the photomultiplier tube: Photons dislodge electrons by striking the photocathode, and these electrons strike a chain of dynodes, increasing the electric signal.
2. Function of a photomultiplier tube (PMT): It converts a light pulse into an electrical signal of measurable magnitude.
3. How a photomultiplier tube works: It is a photoemissive device where the absorption of a photon results in the emission of an electron, amplifying the electrons generated by a photocathode.
4. Typical gain of a PMT: Current gains are usually three to five, resulting in an average of four electrons leaving the first dynode with a variance of about two electrons.
5. Photomultiplier tubes as detectors: They are highly sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges, belonging to the class of vacuum phototubes.
6. High sensitivity of photomultipliers: They have a very high sensitivity due to an avalanche multiplication process and also exhibit a high detection bandwidth.
7. Job title of a PMT: Senior Product Manager-Technical (PMT) responsible for owning software, hardware, or technical services.
8. Testing a PMT: The PMTs are tested by flashing a very dim LED light in a dark box using the lowest possible voltage, with quick flashes and short durations.
Questions and Answers:
1. How does the photomultiplier work?
The working principle of the photomultiplier tube is that photons will dislodge electrons by striking the photocathode. These electrons will then strike a chain of dynodes, which dislodges more electrons, increasing the electric signal that is proportional to the initial electromagnetic radiation in the sample.
2. What does a PMT do?
A photomultiplier tube (PMT) converts a light pulse into an electrical signal of measurable magnitude.
3. Which best describes how a photomultiplier tube works?
A photomultiplier tube, useful for light detection of very weak signals, is a photoemissive device in which the absorption of a photon results in the emission of an electron. These detectors work by amplifying the electrons generated by a photocathode exposed to a photon flux.
4. What is the typical gain of a PMT?
Typical current gains are three to five, so there will typically be four electrons leaving the first dynode, with a variance of about two electrons. This large relative variance (due to the small number of ejected electrons) gives rise to large variations in the pulse height of the detected signal.
5. Is PMT a detector?
Photomultiplier tubes (photomultipliers or PMTs for short) are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are members of the class of vacuum tubes, more specifically vacuum phototubes.
6. Why is a photomultiplier so sensitive?
Photomultipliers (sometimes called photon multipliers) are a type of photoemissive detectors which have a very high sensitivity due to an avalanche multiplication process and also exhibit a high detection bandwidth.
7. What is a PMT job title?
As a Senior Product Manager– Technical (PMT), you’ll be the end-to-end owner of one of our software, hardware, or technical services.
8. How do you test a PMT?
The PMTs are tested by flashing a very dim LED light in the dark box with them. The LED is activated using the lowest possible voltage to emit the smallest number of photons possible. The light flashes very quickly (at roughly 10 Hz) and remains lit for only 11ns at a time.
How does the photomultiplier work
The working principle of the photomultiplier tube is that photons will dislodge electrons by striking the photocathode. These electrons will then strike a chain of dynodes, which dislodges more electrons, increasing the electric signal that is proportional to the initial electromagnetic radiation in the sample.
Cached
What does a PMT do
A photomultiplier tube (PMT) converts a light pulse into an electrical signal of measurable magnitude.
Which best describes how a photomultiplier tube works
A photomultiplier tube, useful for light detection of very weak signals, is a photoemissive device in which the absorption of a photon results in the emission of an electron. These detectors work by amplifying the electrons generated by a photocathode exposed to a photon flux.
CachedSimilar
What is the typical gain of a PMT
Typical current gains are three to five, so there will typically be four electrons leaving the first dynode, with a variance of about two electrons. This large relative variance (due to the small number of ejected electrons) gives rise to large variations in the pulse height of the detected signal.
Is PMT a detector
Photomultiplier tubes (photomultipliers or PMTs for short) are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are members of the class of vacuum tubes, more specifically vacuum phototubes.
Why is a photomultiplier so sensitive
Photomultipliers (sometimes called photon multipliers) are a type of photoemissive detectors which have a very high sensitivity due to an avalanche multiplication process, and also exhibit a high detection bandwidth.
What is a PMT job title
As a Senior Product Manager– Technical (PMT), you'll be the end-to-end owner of one of our software, hardware, or technical services.
How do you test a PMT
The PMTs are to be tested by flashing a very dim LED light in the dark box with them. The LED is activated using the lowest possible voltage to emit the smallest number of photons possible. The light flashes very quickly (at roughly 10 Hz) and remains lit for only 11ns at a time.
What is the structure of the PMT
The PMT consists of a photocathode to convert incident photons to electrons, focusing optics to focus the electrons onto the first dynode, a cascade of dynodes that multiply the electron, and an anode to collect the now numerous electrons.
Is a photomultiplier tube a detector
Photomultiplier tubes (photomultipliers or PMTs for short) are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum.
What is PMT structure
The PMT consists of a photocathode to convert incident photons to electrons, focusing optics to focus the electrons onto the first dynode, a cascade of dynodes that multiply the electron, and an anode to collect the now numerous electrons.
What happens when the gain is increased on a PMT
Increasing PMT gain will increase the intensity of the image. The following example is specific to Cy3 and Cy5, but the logic applies to other laser configurations. If the slide has control spots, adjust PMT voltage so that the control spot color is clearly yellow.
What does PMT mean on an analyzer
Photomultiplier tubes
Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) have long been the preferred detector choices for high- end spectrometers used by primary metal producers and other demanding users. A legacy vacuum tube technology, a PMT detector consists of an evacuated glass housing enclosing several light-detection elements.
What is the disadvantage of photomultiplier
The advantage of the photomultiplier tube is its ability to measure relatively small amounts of electromagnetic radiation because of the amplification process that occurs. A disadvantage is that any spurious signal such as stray radiation is also amplified in the process, leading to an enhancement of the noise.
What is the dark noise in PMT
In principle, when PMTs are working at typical recommended high voltage (HV), the dark noise of PMTs is mainly generated by thermionic electrons emitted from either the cathode or dynodes.
What is a PMT at Amazon
Amazon has two separate product roles, Product Managers (PMs) and Product Managers-Technical (PMTs). As the name implies, PMTs work on more technical products like AWS and usually have computer science or engineering experience. On the other hand, PMs have a more diverse background and work across verticals.
What does PMT meeting mean
PROJECT MANAGEMENT TEAM (PMT): Provides day-to-day, management-level guidance for collaborative planning, design, and construction of the project to achieve the project objective. The PMT is responsible for all project progress and for developing benchmarks, metrics, or standards for progress evaluation.
What does a photomultiplier or PMT detect
Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) are generally used as the photodetectors because of their fast response, high gain, and high signal-to-noise ratio. They are sensitive for detection of light in the UV, visible, and near-IR region of ∼200–900 nm.
How to calculate PMT
The number of periods is expressed in years right. 30 years. But we are trying to calculate a monthly payment. And that's why our monthly payment amount looks so weird this is actually an annual
What PMT means in finance
payment per period
Payment (PMT)
This is the payment per period. To calculate a payment the number of periods (N), interest rate per period (i%) and present value (PV) are used.
What is a PMT detector
3.3 Detector
Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) are generally used as the photodetectors because of their fast response, high gain, and high signal-to-noise ratio. They are sensitive for detection of light in the UV, visible, and near-IR region of ∼200–900 nm.
What are the pros and cons of PMT
The advantage of the photomultiplier tube is its ability to measure relatively small amounts of electromagnetic radiation because of the amplification process that occurs. A disadvantage is that any spurious signal such as stray radiation is also amplified in the process, leading to an enhancement of the noise.
What is PMT analysis
The PMT analyzes test data in accordance with applicable standards and sound statistical methodology; and, The PMT validates or invalidates the applicant's results and conclusions based on the data.
What is PMT in a contract
The PMT is a contract performance management system that accurately captures and reports engineering system performance against agreed capability requirements including contract business rules and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) which help ensure that the personnel involved can deliver on both the organization's …
What is the output of a PMT
The PMT Signal
The output pulse for a single photoelectron is called the 'Single Electron Response' or SER of the PMT. Some typical SER shapes are shown in the figure below. Due to the random nature of the PMT gain, Iser is not stable but varies from pulse to pulse.