Summary of the Article: Dynodes and Photocathodes
1. The dynode is a metal plate containing a substance, such as a bialkali compound, that emits secondary electrons upon impact with accelerated electrons. The acceleration of the photoelectrons and their impact on the dynode produce multiple secondary electrons.
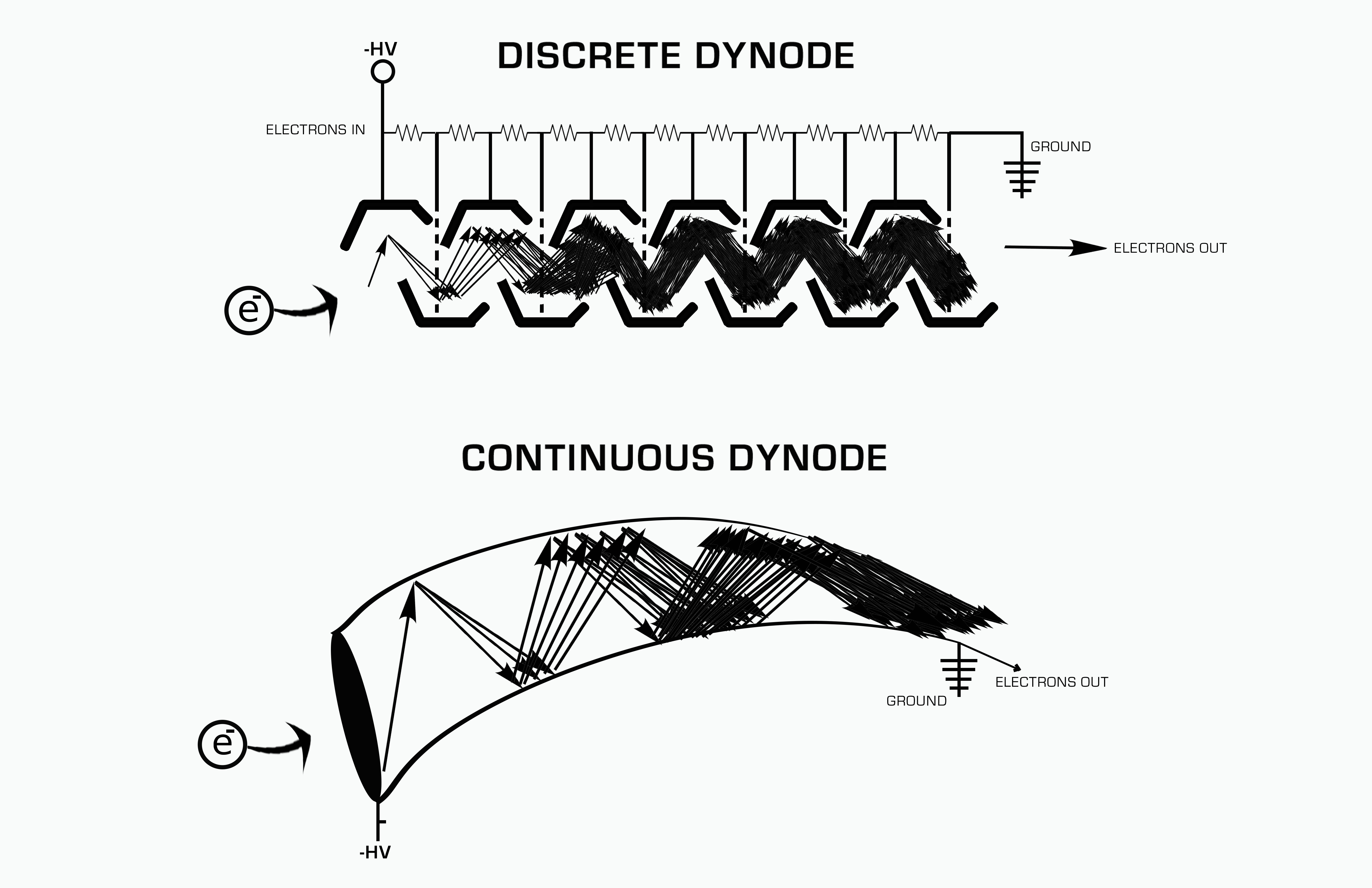
2. An example of a dynode is the electron multiplier, where electrodes called dynodes are arranged in such a way that each succeeding generation of electrons is attracted to the next dynode.
3. The voltage of the dynode is maintained at 90 to 100 V positive with respect to the cathode. Each accelerated photoelectron that strikes the dynode surface produces several electrons.
4. Dynode signals are positive, while anode signals are negative. These signals are shown on the interface of the DRS4 module in modern physics experiments, which use Digital Pulse Processing (DPP) modules to process the original signals from detectors.
5. A photocathode is a negatively charged electrode coated with a photosensitive compound, commonly used in light detection devices such as image intensifiers. When struck by light photons, the absorbed energy causes electron emission through the photoelectric effect.
6. Photocathodes are typically made of alkali-metal films, including potassium bromide (KBr), cesium telluride (CsTe), cesium iodide (CsI), or rubidium telluride (RbTe).
7. The term “dynode” refers to an electrode in an electron tube that functions to produce secondary emission of electrons.
Questions:
1. What is the dynode made of?
A: The dynode is made of a metal plate containing a substance, such as a bialkali compound. It emits secondary electrons upon impact with accelerated electrons.
2. Can you give an example of a dynode?
A: Yes, an example of a dynode is the electron multiplier. In this device, electrodes called dynodes are arranged so that each succeeding generation of electrons is attracted to the next dynode.
3. What is the voltage of the dynode?
A: The dynode is maintained at a voltage of 90 to 100 V positive with respect to the cathode. Each accelerated photoelectron that strikes the dynode surface produces several electrons.
4. Are dynode signals positive or negative?
A: Dynode signals are positive, while anode signals are negative. In modern physics experiments, Digital Pulse Processing (DPP) modules are used to process these signals from detectors.
5. How does a photocathode work?
A: A photocathode is a negatively charged electrode coated with a photosensitive compound. When struck by light photons, the absorbed energy causes electron emission through the photoelectric effect.
6. What materials are used as photocathodes?
A: Photocathodes are typically made of alkali-metal films, such as potassium bromide (KBr), cesium telluride (CsTe), cesium iodide (CsI), or rubidium telluride (RbTe).
7. What is the function of a dynode?
A: A dynode is an electrode in an electron tube that produces secondary emission of electrons.
Note: The format shown here is a representation of the requested HTML format, but may not contain the exact line breaks and `
` tags as described.
What is the dynode made of
The dynode is made of a metal plate containing a substance on the surface such as a bialkali compound, which emits secondary electrons upon impact with accelerated electrons. The acceleration of the photoelectrons and the impact of these on the dynode produce multiple secondary electrons.
What is an example of a dynode
electron multiplier
Electrodes, called dynodes, are so arranged that each succeeding generation of electrons is attracted to the next dynode. For example, if 4 electrons are released at the first dynode, then 16 will emerge from the second and so forth.
CachedSimilar
What is the voltage of the dynode
The electrons emitted from the cathode are accelerated toward the first dynode, which is maintained 90 to 100 V positive concerning the cathode. Each accelerated photoelectron that strikes the dynode surface produces several electrons.
CachedSimilar
Is dynode positive or negative
Dynode (positive) and anode (negative) signals are shown on the interface of the DRS4 module. Digital Pulse Processing (DPP) modules are being used to replace the analog electronics modular in modern physics experiments for processing the original signals from detectors.
How does a photocathodes work
A photocathode is a negatively charged electrode in a light detection device such as the input screen in an image intensifier (II) that is coated with a photosensitive compound. When this is struck by light photons, the absorbed energy causes electron emission due to the photoelectric (PE) effect.
What materials are used as photocathode
Photocathodes are typically made of alkali-metal films such as potassium bromide (KBr), cesium telluride (CsTe), cesium iodide (CsI), or rubidium telluride (RbTe).
What material is used for photocathode
Photocathodes are typically made of alkali-metal films such as potassium bromide (KBr), cesium telluride (CsTe), cesium iodide (CsI), or rubidium telluride (RbTe).
What is meant by dynode
dy·node ˈdī-ˌnōd. : an electrode in an electron tube that functions to produce secondary emission of electrons.
What is a high energy dynode
A. This unique high energy dynode (HED) multiplier is designed to be sensitive to a very wide range of ion energies. While this is critical for ion trap operation, it will also enhance the performance of quadrupole systems operating at high mass.
How many dynodes does a photomultiplier tube have
The process is continued usually up to 9 dynodes (or stages) until the anode is reached.
What materials are used as a photocathode
Photocathodes are typically made of alkali-metal films such as potassium bromide (KBr), cesium telluride (CsTe), cesium iodide (CsI), or rubidium telluride (RbTe).
How do you make a photocathode
It can be relatively simply fabricated by evaporating an antimony film onto a glass plate and then evaporating cesium onto it.
What is the purpose of a Dynode in a photomultiplier tube
In a PMT, dynodes are electrodes in a vacuum tube that serve as an electron multiplier through SEE (see Figure 1). The dynodes are so arranged that the electric fields between them cause the electrons emitted by each dynode to strike the next with an energy of a few hundred eV.
How does a Faraday cup work
The Faraday cup utilizes a physical principle according to which the electrical charges delivered to the inner surface of a hollow conductor are redistributed around its outer surface due to mutual self-repelling of charges of the same sign – a phenomenon discovered by Faraday.
What is a conversion dynode
A conversion dynode is sometimes put in front of the electron multiplier. This dynode, on which a high voltage of 5 to 20 kV with reverse polarity to the ion is applied, makes it possible to detect negative ions and increase the signal intensity of ions, particularly in the high mass region.
How does a photomultiplier tube works
A photomultiplier tube, useful for light detection of very weak signals, is a photoemissive device in which the absorption of a photon results in the emission of an electron. These detectors work by amplifying the electrons generated by a photocathode exposed to a photon flux.
What is the working principle of the photomultiplier tube
The working principle of the photomultiplier tube is that photons will dislodge electrons by striking the photocathode. These electrons will then strike a chain of dynodes, which dislodges more electrons, increasing the electric signal that is proportional to the initial electromagnetic radiation in the sample.
What is the working principle of the photomultiplier
The working principle of the photomultiplier tube is that photons will dislodge electrons by striking the photocathode. These electrons will then strike a chain of dynodes, which dislodges more electrons, increasing the electric signal that is proportional to the initial electromagnetic radiation in the sample.
How does a photomultiplier work
A photomultiplier tube, useful for light detection of very weak signals, is a photoemissive device in which the absorption of a photon results in the emission of an electron. These detectors work by amplifying the electrons generated by a photocathode exposed to a photon flux.
Does a microwave work like a Faraday cage
Common cell phone frequency is 700 MHz ● Common WiFi frequency is 2.4 GHz ● Most Microwaves operate at 2.45 GHz ● Microwaves work as Faraday cages to keep microwaves that heat your food from escaping.
Will a cell phone ring in a Faraday bag
The phone will not ring, and the call will go to voicemail.
How does the conversion process work
The conversion process searches for the first rule that matches the incoming data, and then applies the action associated with that rule. The output of that action can then be further processed by other rules, depending on its type-out value and whether other rules exist that are triggered by that value.
What is the purpose of a dynode in a photomultiplier tube
In a PMT, dynodes are electrodes in a vacuum tube that serve as an electron multiplier through SEE (see Figure 1). The dynodes are so arranged that the electric fields between them cause the electrons emitted by each dynode to strike the next with an energy of a few hundred eV.
What is the photomultiplier tube in simple words
photomultiplier tube, electron multiplier tube that utilizes the multiplication of electrons by secondary emission to measure low light intensities. It is useful in television camera tubes, in astronomy to measure intensity of faint stars, and in nuclear studies to detect and measure minute flashes of light.
What is photomultiplier tube in simple words
photomultiplier tube, electron multiplier tube that utilizes the multiplication of electrons by secondary emission to measure low light intensities. It is useful in television camera tubes, in astronomy to measure intensity of faint stars, and in nuclear studies to detect and measure minute flashes of light.