Key Points:
1. To determine the number of elements in A U B, use the formula n(A U B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A ∩ B).
2. The formula for the number of elements in A intersection B is n(A∩B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A U B).
3. To find A intersection B intersection C, find the intersection of the elements of set A and set B, then find the intersection of the elements of set B and set C, and finally find the intersection of the two outcomes.
4. In probability, the formula for P(A∪B) is P(A∪B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A∩B), where P(A) is the probability of event A happening, P(B) is the probability of event B happening, and P(A∩B) is the probability of both A and B happening.
5. An example of A U B is A U B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. A union B complement is given by (A ∪ B)’ = U – (A ∪ B).
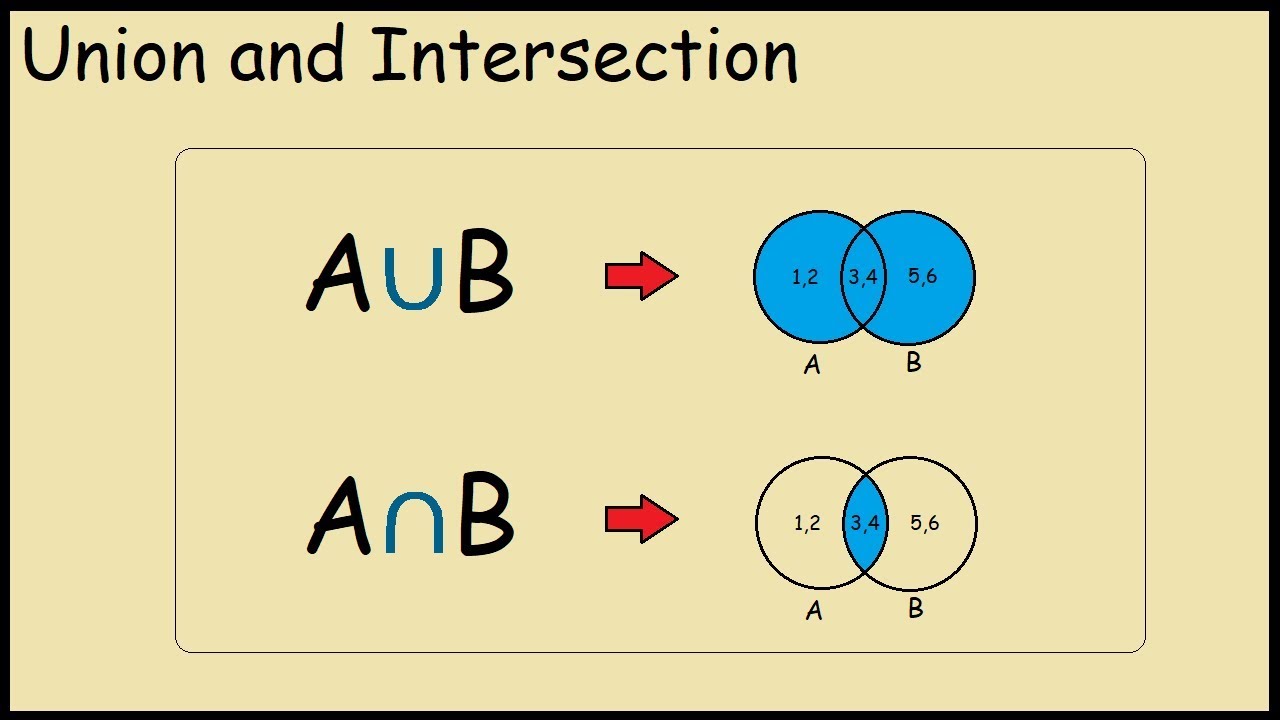
6. In math, ∪ represents the union of two sets, while ∩ represents the intersection of two sets.
7. A ∩ B is the intersection of sets A and B, which is the set of objects that are members of both A and B.
8. A ∩ B ∪ C is the intersection of sets A and B union C, which is obtained by taking the intersection of set A and the set B U C.
9. A ∩ B ∩ C is the intersection of sets A, B, and C, and it consists of the elements that appear in all three sets.
Questions:
- How do you identify the elements of A U B?
- How do you find A∩ B?
- How do you find A∩B∩C?
- How do you find AUB in probability?
- What is an example of AUB?
- What does ∩ and ∪ mean in math?
- What is A∩B in math?
- What is A∩B∪C?
- What are the elements in A ∩ B ∩ C?
Answer: To determine the number of elements in A U B, we will use the formula n(A U B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A ∩ B). Hence, the number of elements in A union B is 19.
Answer: The formula for the number of elements in A intersection B is n(A∩B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A U B).
Answer: To find A intersection B intersection C, first find the intersection of the elements of set A and set B (A ∩ B). Then find the intersection of the elements of set B and set C. Finally, find the intersection of the two outcomes of intersection elements.
Answer: The P(A∪B) formula is given as P(A∪B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A∩B), where P(A) is the probability of event A happening, P(B) is the probability of event B happening, and P(A∩B) is the probability of both A and B happening.
Answer: A U B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. If A union B complement is given by (A ∪ B)’, it can be calculated as U – (A ∪ B).
Answer: ∪ represents the union of two sets, while ∩ represents the intersection of two sets. A complete Venn diagram represents the union of two sets, while the intersection shows what items are shared between categories.
Answer: Intersection of the sets A and B, denoted A ∩ B, is the set of all objects that are members of both A and B. For example, the intersection of {1, 2, 3} and {2, 3, 4} is the set {2, 3}.
Answer: A intersection B union C is represented as A n B U C. It can be obtained by taking the intersection of set A and the set B U C. Hence, we can write A n B U C = A n (B U C).
Answer: If A, B, and C are sets, their intersection A ∩ B ∩ C is the set whose elements are those objects appearing in all three sets. For example, if A = {1, 2, 3, 4}, B = {2, 4, 6}, and C = {3, 4, 5, 6}, the intersection A ∩ B ∩ C would be the set {4}.
How do you identify the elements of AUB
Solution: To determine the number of elements in A U B, we will use the formula n(A U B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A ∩ B). Answer: Hence, the number of elements in A union B is 19.
How do you find A∩ B
The formula for number of elements in A intersection B is n(A∩B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A U B)
How do you find A∩B∩C
How To Find A Intersection B Intersection CFirst, we need to find the intersection of the elements of set A and set B. The is represented as A n B.Second, we need the intersection of the elements of set B and set C.The third and final step is to find the intersection of the two outcomes of intersection elements.
How do you find AUB in probability
he P(A∪B) formula is given as, P(A∪B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A∩B), where P(A) is Probability of event A happening, P(B) is Probability of event B happening, and P(A∩B) is Probability of happening of both A and B.
What is an example of AUB
A union B Complement Examples
A U B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, then A union B complement is given by, (A ∪ B)' = U – (A ∪ B)
What does ∩ and ∪ mean in math
∪: Union of two sets. A complete Venn diagram represents the union of two sets. ∩: Intersection of two sets. The intersection shows what items are shared between categories.
What is A∩B in math
Intersection of the sets A and B , denoted A ∩ B , is the set of all objects that are members of both A and B . The intersection of {1, 2, 3} and {2, 3, 4} is the set {2, 3} .
What is A∩B ∪ C
A intersection B union C is represented as A n B U C. A intersection B union C. The set A n B U C can be obtained by taking the intersection of set A and the set B U C, and hence we can write A n B U C = A n (B U C). Let us learn more about A intersection B union C, and how to solve it, with the help of examples, FAQs.
What are the elements in A ∩ B ∩ C
If A and B and C are sets, their intersection A ∩ B ∩ C is the set whose elements are those objects which appear in A and B and C i.e. those elements appearing in all three sets. Example If A = {1,2,3,4}, B = {2,4,6,8} and C = {3,4,5,6}. List the elements of the set A ∩ B ∩ C. A ∩ B = {2,4} so A ∩ B ∩ C = {4}.
What does A∩B mean in probability
Joint probability: p(A ∩B). Joint probability is that of event A and event B occurring. It is the probability of the intersection of two or more events. The probability of the intersection of A and B may be written p(A ∩ B).
What is an example of ∩ in math
For any two sets A and B, the intersection, A ∩ B (read as A intersection B) lists all the elements that are present in both sets (common elements of A and B). For example, if Set A = {1,2,3,4,5} and Set B = {3,4,6,8}, A ∩ B = {3,4}.
What is an example of ∩
The intersection of two sets A and B, denoted by A∩B, consists of all elements that are both in A and_ B. For example, {1,2}∩{2,3}={2}. In Figure 1.5, the intersection of sets A and B is shown by the shaded area using a Venn diagram.
What does A∩B mean
intersection operation
The intersection operation is denoted by the symbol ∩. The set A ∩ B—read “A intersection B” or “the intersection of A and B”—is defined as the set composed of all elements that belong to both A and B.
What does A∩B mean in math
intersection operation
The intersection operation is denoted by the symbol ∩. The set A ∩ B—read “A intersection B” or “the intersection of A and B”—is defined as the set composed of all elements that belong to both A and B.
What is A∩B
The set A ∩ B—read “A intersection B” or “the intersection of A and B”—is defined as the set composed of all elements that belong to both A and B.
What is A∩B example
For any two sets A and B, the intersection, A ∩ B (read as A intersection B) lists all the elements that are present in both sets (common elements of A and B). For example, if Set A = {1,2,3,4,5} and Set B = {3,4,6,8}, A ∩ B = {3,4}.
How do you identify a mathematical statement
Brielfy a mathematical statement is a sentence which is either true or false. It may contain words and symbols. For example “The square root of 4 is 5" is a mathematical statement (which is, of course, false).
What is the most difficult branch of mathematics
Advanced Calculus is the hardest math subject, according to college professors. One of the main reasons students struggle to understand the concepts in Advanced Calculus is because they do not have a good mathematical foundation. Calculus builds on the algebraic concepts learned in previous classes.
What is a typical example
(tɪpɪkəl ) adjective. You use typical to describe someone or something that shows the most usual characteristics of a particular type of person or thing, and is therefore a good example of that type.
What is called example
Some common synonyms of example are case, illustration, instance, sample, and specimen. While all these words mean "something that exhibits distinguishing characteristics in its category," example applies to a typical, representative, or illustrative instance or case.
What are examples of A∩B
For any two sets A and B, the intersection, A ∩ B (read as A intersection B) lists all the elements that are present in both sets (common elements of A and B). For example, if Set A = {1,2,3,4,5} and Set B = {3,4,6,8}, A ∩ B = {3,4}.
How do you identify a statement as an expression or equation
The best way, to identify, whether a given problem is an expression or equation is that if it contains an equal to sign (=) it is an equation. However, if it does not contain an equal to (=) sign, then it is just an expression.
What is an example of a universal statement
A universal statement says that a certain property is true of all elements in a set. e.g., All positive numbers are greater than zero. All swans are white.
What is the easiest math class in college
What is the Easiest Math Class in CollegeStatistics: Statistics is a branch of mathematics dealing with the collection, analysis, and interpretation of numerical data.Finite Math: Finite math refers to a variety of math courses that do not involve calculus.
What is harder than calculus
At an advanced level, statistics is considered harder than calculus, but beginner-level statistics is much easier than beginner calculus. Frankly, it mostly depends upon the student's interest as some students find it hard to comprehend statistics while others find it hard to understand calculus.