Summary of the Article:
1. Arterial roads and collector streets serve different purposes when it comes to traffic movement. Arterial roads are major corridors for traffic and are important for pedestrians and cyclists.
2. Primary roads are those that fall under the jurisdiction of the department, both within and outside municipalities.
3. There are three main classifications of roadways: arterial, collector, and local roads. The classification depends on the character of traffic and the degree of land access they allow.
4. The classification of roads helps in planning appropriate design components for each type of facility, ensuring a well-designed roadway system.
5. To identify an arterial road, pay attention to the speed limit and intersections. Arterial roads generally have speed limits above 45 MPH and eventually lead to freeways.
6. Non-arterial roads are those that are not freeways or arterial roads.
7. Secondary roads serve interdistrict traffic between urban and rural centers and provide connections between primary roads or major arterial highways.
8. A secondary road is also known as a feeder road or a road of secondary importance.
9. Roadway functional classification refers to the categorization of roads based on their function and purpose.
Questions and Detailed Answers:
- Question: What is the difference between an arterial road and a local road?
- Question: What is the definition of a primary road?
- Question: What are the three main classifications of roadways?
- Question: Why do we classify roads?
- Question: How do you tell if a road is an arterial?
- Question: What is a non-arterial road?
- Question: What are considered secondary roads?
- Question: What is a secondary road called?
- Question: What is a roadway functional classification?
An arterial road is a major corridor for traffic movement, including pedestrians and cyclists. Collector streets collect and distribute traffic between local streets and arterial roads.
Primary roads are roads and streets under department jurisdiction, both inside and outside municipal boundaries.
The three main classifications of roadways are arterial, collector, and local roads. Each classification depends on the character of traffic and land access.
Roads are classified to plan appropriate design components for each type of facility and ensure a well-designed roadway system.
An arterial road can be identified by its speed limits and intersections. Speed limits above 45 MPH and roads leading to freeways are indicative of arterial roads.
A non-arterial road is a state road that is neither a freeway nor an arterial road.
Secondary roads serve interdistrict traffic between urban and rural centers and provide connections between primary roads or major arterial highways.
A secondary road is also known as a feeder road or a road of secondary importance.
Roadway functional classification refers to the categorization of roads based on their function and purpose.
What is the difference between an arterial road and a local road
Collector streets serve to collect and distribute traffic between local streets and arterial roads. Arterial roads (with the expressway system) provide the major corridors for traffic (including surface transit) movement. Arterial roads are also important for pedestrians and cyclists.
What is the definition of a primary road
“Primary roads” or “primary road system” means those roads and streets both inside and outside the boundaries of municipalities which are under department jurisdiction.
What are the three main classifications of roadways
There are three highway functional classifications: arterial, collector, and local roads. All streets and highways are grouped into one of these classes, depending on the character of the traffic (i.e., local or long distance) and the degree of land access that they allow.
Why do we classify roads
Roads or highways are functionally classified in order help plan appropriate design components for each type of facility. A well-designed roadway system has a mix of roadway types. Each roadway type is designated based on its need or priority for access or mobility.
Cached
How do you tell if a road is an arterial
For the everyday motorist, the easiest way to identify an arterial road is by speed limits and intersections. Anything below 45 MPH is most likely a local or collector road and anything between 45-55 MPH that eventually leads to a freeway is most likely an arterial road.
What is a non arterial road
non-arterial State road means a State road which is not a freeway or an arterial road; Sample 1Sample 2.
What are considered secondary roads
Secondary road or highway means a highway which serves interdistrict traffic between urban and rural centers and provides traffic connections between primary roads or major arterial highways.
What is a secondary road called
noun. Synonyms of secondary road. : a road not of primary importance. : a feeder road.
What is a roadway functional classification
Functional classification is an ordering system that defines “the part that any particular road or street should play in serving the flow of trips through a highway network.” Functional classification categorizes streets according to their ability to 1) move traffic, and 2) provide access to adjacent properties.
What is a freeway vs highway
The quick answer is all freeways are highways, but not all highways are freeways. It may sound like a riddle, but it doesn't have to be confusing. A freeway is a highway where access to the roadway is controlled. Drivers can only enter a controlled-access highway by ramps.
What makes a road a road
So a 'road' is anything that connects two points, while 'streets' are public ways which have buildings on either side. Avenues, meanwhile, have the same attributes as streets but run perpendicular to them, while a boulevard is essentially a wide street (or avenue), with a median through the middle.
What are the characteristics of roads
The primary features of roads include lanes, sidewalks (pavement), roadways (carriageways), medians, shoulders, verges, bike paths (cycle paths), and shared-use paths.
What are the different types of arterial roads
Arterial roads are major through roads that carry large amounts of traffic from collectors to interstates. These roads are a supplement to interstates and examples can be freeways or highways too.
How do you identify arterial roads
For the everyday motorist, the easiest way to identify an arterial road is by speed limits and intersections. Anything below 45 MPH is most likely a local or collector road and anything between 45-55 MPH that eventually leads to a freeway is most likely an arterial road.
What do you call a road without asphalt
A dirt road or track is a type of unpaved road not paved with asphalt, concrete, brick, or stone; made from the native material of the land surface through which it passes, known to highway engineers as subgrade material.
What is the middle of two roads called
The median strip, central reservation, roadway median, or traffic median is the reserved area that separates opposing lanes of traffic on divided roadways such as divided highways, dual carriageways, freeways, and motorways.
What is secondary road or street
SECONDARY STREET means in the case of a premise that has access from more than one public road, a road that is not the primary street but which intersects with or adjoins that road, but does not include a laneway.
What are A and B roads
an A road will generally be among the widest, most direct roads in an area, and will be of the greatest significance to through traffic. A B road will still be of significance to traffic (including through traffic), but less so than an A road.
How do you identify primary secondary and tertiary roads
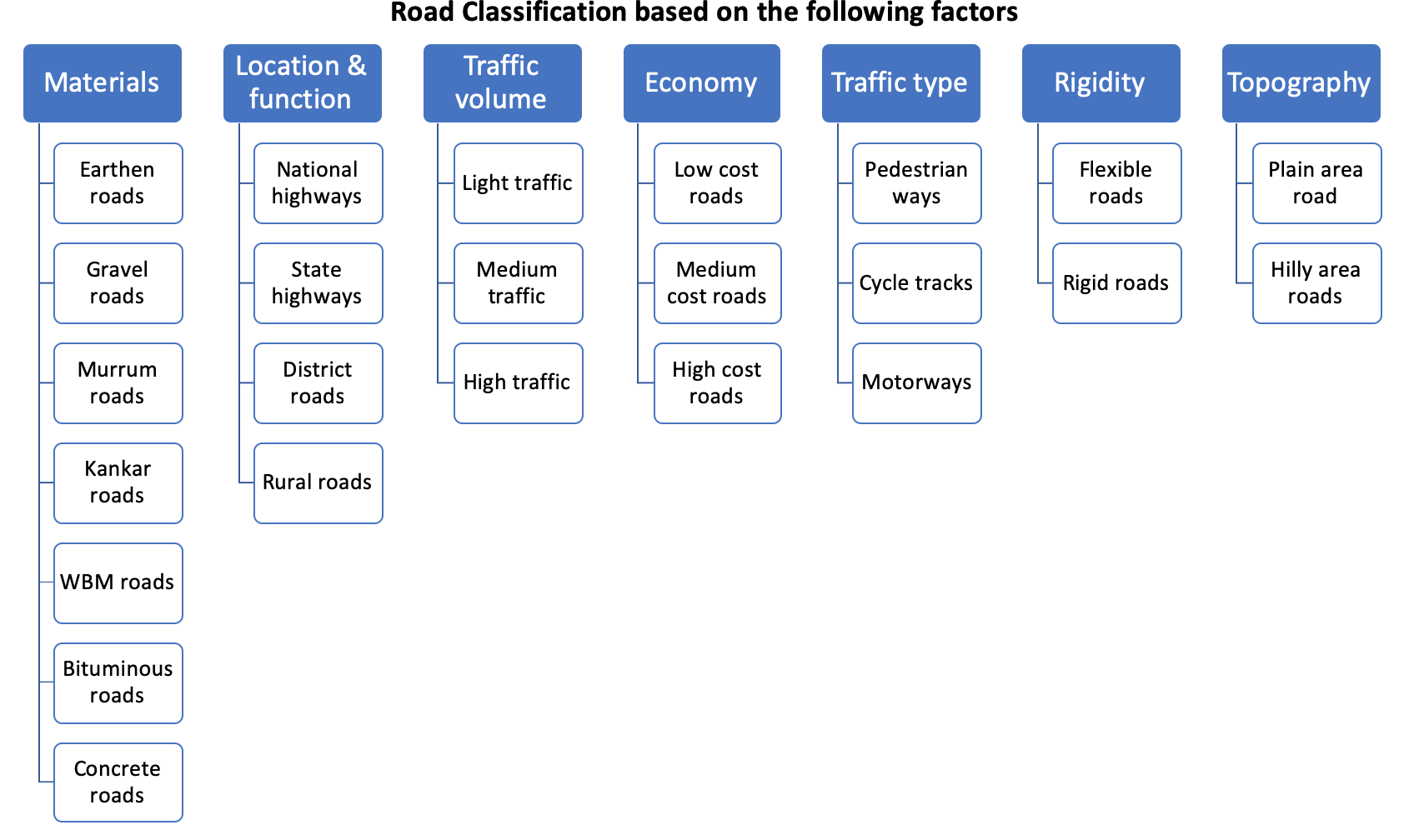
Tertiary System.Primary System : Express Ways. National Highways (NH) (a) Express Ways :Secondary System : The secondary system consists of two categories of roads. State Highways (SH)Tertiary System : The tertiary system are rural roads and these consists of two categories of roads : Other District Roads (ODR)
What are the different functional classifications
Functional ClassificationInterstates. Interstates are the highest classification of Arterials and are designed and constructed with mobility and long-distance travel in mind.Principal Arterials.Minor Arterials.Collector Streets.Local Streets.
What are the functional classifications
Functional classification is an ordering system that defines “the part that any particular road or street should play in serving the flow of trips through a highway network.” Functional classification categorizes streets according to their ability to 1) move traffic, and 2) provide access to adjacent properties.
What is the difference between a highway and a parkway
A "highway" is a strip of public land devoted to movement over which the abutting property owners have the right of light, air and access. A "parkway" is a strip of public land devoted to recreation over which the abutting property owners have no right of light, air or access.
Why is an interstate called a highway
The Interstate Highway System is named after President Eisenhower, who believed a reliable system of freeways was necessary for the economic development and defense of the U.S. The Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956 authorized construction, which was completed over the course of the next 35 years.
What is a simple definition of a road
: an open way for vehicles, persons, and animals. especially : one lying outside of an urban district : highway. : roadbed sense 2b. 3. : a route or way to an end, conclusion, or circumstance.
What is the difference between a road and a roadway
A road includes the whole thing, from shoulder to shoulder, including parts that can't be driven on (parking spaces, bike lanes). A "roadway" is only that portion of a road intended for normal vehicular traffic.