Summary of the Article: Why Do Humans Exhale Carbon Dioxide?
1. Do humans exhale carbon dioxide or monoxide?
When we take a breath, we pull air into our lungs that contains mostly nitrogen and oxygen. However, when we exhale, we breathe out mostly carbon dioxide.
2. Why do humans breathe out carbon dioxide?
We need to breathe in order to live because we require oxygen to convert glucose into energy. Carbon dioxide is the waste product of this process.
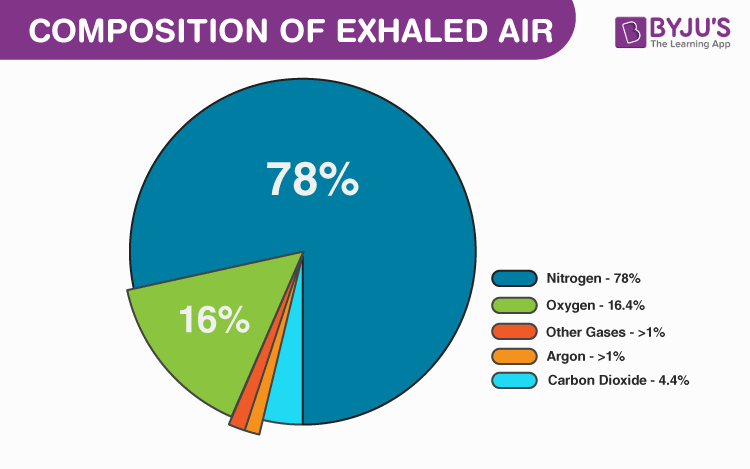
3. What gases do humans exhale?
Exhaled air contains nitrogen (78%), oxygen (17%), carbon dioxide (4%), and other gases (1%).
4. How is carbon dioxide excreted from the body?
Once the venous blood returns to the lungs, carbon dioxide diffuses out of the bloodstream, through the capillaries, and into the alveoli. From there, it is expelled, while oxygen simultaneously binds with hemoglobin to be carried back to the tissues.
5. What happens if you don’t breathe out carbon dioxide?
If your body is unable to eliminate carbon dioxide, it can accumulate in your blood. This condition, known as hypercapnia, can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath and fatigue.
6. Why do we breathe in oxygen and not carbon dioxide?
Oxygen is essential for various bodily functions such as digestion, muscle movement, and even thinking. Carbon dioxide is a waste product that is produced during these processes. The role of the lungs is to supply the body with oxygen and eliminate carbon dioxide.
7. Is the gas you exhale 100% carbon dioxide?
No, when we exhale, the composition of the air remains similar to that of the inhaled air, with only the percentages of carbon dioxide and oxygen changing. Inhaled air contains 21% oxygen and 0.04% carbon dioxide, while exhaled air contains 16.4% oxygen and 4.4% carbon dioxide.
8. Is carbon dioxide harmful to your body?
Carbon dioxide is considered minimally toxic by inhalation. Its primary health effects are due to its behavior as a simple asphyxiant, which can reduce or displace the normal oxygen in breathing air. Mild exposure to carbon dioxide may lead to symptoms such as headaches and drowsiness.
Questions:
1. Why do humans exhale carbon dioxide?
Humans exhale carbon dioxide because it is a waste product generated during the process of converting glucose into energy.
2. What are the gases present in exhaled air?
Exhaled air contains nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other gases.
3. How is carbon dioxide eliminated from the body?
Carbon dioxide is eliminated from the body by diffusing out of the bloodstream in the lungs and being expelled through exhalation.
4. What can happen if carbon dioxide is not exhaled properly?
If carbon dioxide is not effectively exhaled, it can build up in the blood, leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath and fatigue.
5. What is the role of the lungs in breathing?
The lungs supply the body with oxygen and remove waste gases like carbon dioxide.
6. How does the composition of exhaled air differ from inhaled air?
Exhaled air contains a higher percentage of carbon dioxide and a lower percentage of oxygen compared to inhaled air.
7. Can carbon dioxide be harmful to the body?
Carbon dioxide can be harmful if its concentration in the air is too high, as it can displace oxygen and cause symptoms like headaches and drowsiness.
8. What is hypercapnia?
Hypercapnia is a condition characterized by the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the blood, resulting in symptoms such as shortness of breath and fatigue.
9. Why is oxygen necessary for bodily functions?
Oxygen is essential for processes like digestion, muscle movement, and brain function, as it is required for cellular energy production.
10. What are the symptoms of mild carbon dioxide exposure?
Mild exposure to carbon dioxide may cause symptoms such as headaches and drowsiness.
Do humans exhale carbon dioxide or monoxide
When we take a breath, we pull air into our lungs that contains mostly nitrogen and oxygen. When we exhale, we breathe out mostly carbon dioxide.
Why do humans breathe out carbon dioxide
So you breath to live, because you need the oxygen to turn glucose into energy. Without oxygen the production stops. Carbon Dioxide is the waste product of this process.
Cached
What gases do humans exhale
In turn, exhaled air contains:nitrogen – 78%oxygen – 17%carbon dioxide – 4%other gases – 1%.
How carbon dioxide is excreted from the body
Once the venous blood returns to the lungs, the carbon dioxide diffuses out of the bloodstream, through the capillaries, and into the alveoli from where it is expelled, during which time oxygen simultaneously binds with hemoglobin to be carried back to the tissues.
What happens if you don’t breathe out carbon dioxide
If your body can't get rid of carbon dioxide, a waste product, it can build up in your blood. Hypercapnia can be chronic (long-lasting) and cause symptoms like shortness of breath (dyspnea) and daytime tiredness or fatigue. It can also be acute (sudden or all at once), with much more serious symptoms.
Why do we breathe in oxygen and not carbon dioxide
Everyday functions of the body like digesting your food, moving your muscles or even just thinking, need oxygen. When these processes happen, a gas called carbon dioxide is produced as a waste product. The job of your lungs is to provide your body with oxygen and to get rid of the waste gas, carbon dioxide.
Is the gas you exhale 100% carbon dioxide
When we exhale, the composition of the air remains almost the same as the air we inhale, only the percentage of carbon dioxide and oxygen changes. The amount of inhaled air contains 21% of oxygen and 0.04% of carbon dioxide, while the air we breathe out contains 16.4% of oxygen and 4.4% of carbon dioxide.
Is carbon dioxide harmful to your body
CO2 is considered to be minimally toxic by inhalation. The primary health effects caused by CO2 are the result of its behavior as a simple asphyxiant. A simple asphyxiant is a gas which reduces or displaces the normal oxygen in breathing air. Symptoms of mild CO2 exposure may include headache and drowsiness.
Is carbon dioxide waste in the body
When you burn food for energy, your body makes carbon dioxide as a waste product in the form of a gas. Your blood carries this gas to your lungs. You exhale carbon dioxide and breathe in oxygen thousands of times a day.
What happens if CO2 is not removed from the body
If your body can't get rid of carbon dioxide, a waste product, it can build up in your blood. Hypercapnia can be chronic (long-lasting) and cause symptoms like shortness of breath (dyspnea) and daytime tiredness or fatigue. It can also be acute (sudden or all at once), with much more serious symptoms.
What happens if you breathe in 100% carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide does not only cause asphyxiation by hypoxia but also acts as a toxicant. At high concentrations, it has been showed to cause unconsciousness almost instantaneously and respiratory arrest within 1 min [6]. Other causes of carbon dioxide intoxication have been identified as well, such as dry ice.
Is carbon dioxide harmful to humans
This could occur when exposed to levels above 5,000 ppm for many hours. At even higher levels of CO2 can cause asphyxiation as it replaces oxygen in the blood-exposure to concentrations around 40,000 ppm is immediately dangerous to life and health. CO2 poisoning, however, is very rare.
What happens if we dont exhale carbon dioxide
Buildup of carbon dioxide can damage tissues and organs and prevent or slow oxygen delivery to the body. Respiratory failure can also develop slowly. When it does, it is called chronic respiratory failure.
What would happen if we only breathe carbon dioxide
Symptoms of mild CO2 exposure may include headache and drowsiness. At higher levels,rapid breathing, confusion, increased cardiac output, elevated blood pressure and increased arrhythmias may occur. Breathing oxygen depleted air caused by extreme CO2 concentrations can lead to death by suffocation.
What gas is given off when we exhale
In turn, exhaled air contains:
nitrogen – 78% oxygen – 17% carbon dioxide – 4%
How much CO2 do you exhale with each breath
= 0.0005 kilograms of air per breath. 3.8 carbon dioxide molecules per 10000 air molecules.
What happens when body is full of carbon dioxide
Having too much carbon dioxide in the body can cause nonspecific symptoms like headache, fatigue, and muscle twitches. Often, it clears up quickly on its own. With severe hypercapnia, though, the body can't restore CO2 balance and the symptoms are more serious.
What happens when your body produces too much carbon dioxide
If your body can't get rid of carbon dioxide, a waste product, it can build up in your blood. Hypercapnia can be chronic (long-lasting) and cause symptoms like shortness of breath (dyspnea) and daytime tiredness or fatigue. It can also be acute (sudden or all at once), with much more serious symptoms.
Where does the body get rid of carbon dioxide
lungs
In the human body, carbon dioxide is formed intracellularly as a byproduct of metabolism. CO2 is transported in the bloodstream to the lungs where it is ultimately removed from the body through exhalation.
How does carbon dioxide leave your body
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a waste product of cellular metabolism. You get rid of it when you breathe out (exhale). This gas is transported in the opposite direction to oxygen: It passes from the bloodstream – across the lining of the air sacs – into the lungs and out into the open.
How does the body get rid of carbon dioxide
In the human body, carbon dioxide is formed intracellularly as a byproduct of metabolism. CO2 is transported in the bloodstream to the lungs where it is ultimately removed from the body through exhalation.
What are the symptoms of too much carbon dioxide in the body
As toxicity increases, a person may experience symptoms such as:Drowsiness.Headaches Skin that looks flushed Trouble concentrating or thinking clearly.Dizziness or disorientation Shortness of breath.Hyperventilation.
How much CO2 in the air is lethal
This could occur when exposed to levels above 5,000 ppm for many hours. At even higher levels of CO2 can cause asphyxiation as it replaces oxygen in the blood-exposure to concentrations around 40,000 ppm is immediately dangerous to life and health.
What would happen if you only breathed pure oxygen
Breathing 100 percent oxygen at normal pressure can cause acute oxygen poisoning, which can lead to all sorts of symptoms, including: Fluid in the lungs, hyperventilation or labored breathing. Chest pains, mild burning on inhalation and uncontrollable coughing (sometimes with blood)
What happens if you breathe too much carbon dioxide
At low concentrations, gaseous carbon dioxide appears to have little toxicological effect. At higher concentrations it leads to an increased respiratory rate, tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias and impaired consciousness. Concentrations >10% may cause convulsions, coma and death.
